Surfactant protein A alters endosomal trafficking of influenza A virus in macrophages
- PMID: 36960051
- PMCID: PMC10028185
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.919800
Surfactant protein A alters endosomal trafficking of influenza A virus in macrophages
Abstract
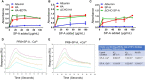
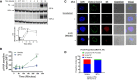
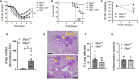
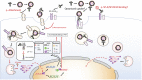
Influenza A virus infection (IAV) often leads to acute lung injury that impairs breathing and can lead to death, with disproportionate mortality in children and the elderly. Surfactant Protein A (SP-A) is a calcium-dependent opsonin that binds a variety of pathogens to help control pulmonary infections by alveolar macrophages. Alveolar macrophages play critical roles in host resistance and susceptibility to IAV infection. The effect of SP-A on IAV infection and antiviral response of macrophages, however, is not understood. Here, we report that SP-A attenuates IAV infection in a dose-dependent manner at the level of endosomal trafficking, resulting in infection delay in a model macrophage cell line. The ability of SP-A to suppress infection was independent of its glycosylation status. Binding of SP-A to hemagglutinin did not rely on the glycosylation status or sugar binding properties of either protein. Incubation of either macrophages or IAV with SP-A slowed endocytic uptake rate of IAV. SP-A interfered with binding to cell membrane and endosomal exit of the viral genome as indicated by experiments using isolated cell membranes, an antibody recognizing a pH-sensitive conformational epitope on hemagglutinin, and microscopy. Lack of SP-A in mice enhanced IFNβ expression, viral clearance and reduced mortality from IAV infection. These findings support the idea that IAV is an opportunistic pathogen that co-opts SP-A to evade host defense by alveolar macrophages. Our study highlights novel aspects of host-pathogen interactions that may lead to better understanding of the local mechanisms that shape activation of antiviral and inflammatory responses to viral infection in the lung.
Keywords: collectin; influenza A virus; lung; macrophages; surfactant protein A.
Copyright © 2023 Yau, Yang, Chen, Umstead, Atkins, Katz, Yewdell, Gandhi, Halstead and Chroneos.
Conflict of interest statement
Author ZC is co-founder of Respana Therapeutic, Inc. (http://respana-therapeutics.com/), an early-stage company developing immune-therapeutics. Author ZC and The Pennsylvania State University own equity in Respana Therapeutics. These financial interests have been reviewed by the University’s Institutional and Individual Conflict of Interest Committees and are currently being managed by the University. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

