Pleiotropic antifibrotic actions of aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 in the lungs
- PMID: 36960058
- PMCID: PMC10030054
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.886601
Pleiotropic antifibrotic actions of aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 in the lungs
Abstract
Introduction: Pulmonary fibrosis is a destructive, progressive disease that dramatically reduces life quality of patients, ultimately leading to death. Therapeutic regimens for pulmonary fibrosis have shown limited benefits, hence justifying the efforts to evaluate the outcome of alternative treatments.
Methods: Using a mouse model of bleomycin (BLM)-induced lung fibrosis, in the current work we asked whether treatment with pro-resolution molecules, such as pro-resolving lipid mediators (SPMs) could ameliorate pulmonary fibrosis. To this end, we injected aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 (7S,8R,17R-trihydroxy-4Z,9E,11E,13Z,15E19Z-docosahexaenoic acid; ATRvD1; i.v.) 7 and 10 days after BLM (intratracheal) challenge and samples were two weeks later.
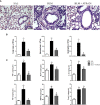
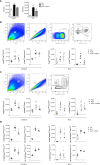
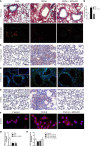
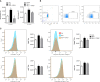
Results and discussion: Assessment of outcome in the lung tissues revealed that ATRvD1 partially restored lung architecture, reduced leukocyte infiltration, and inhibited formation of interstitial edema. In addition, lung tissues from BLM-induced mice treated with ATRvD1 displayed reduced levels of TNF-α, MCP-1, IL-1-β, and TGF-β. Of further interest, ATRvD1 decreased lung tissue expression of MMP-9, without affecting TIMP-1. Highlighting the beneficial effects of ATRvD1, we found reduced deposition of collagen and fibronectin in the lung tissues. Congruent with the anti-fibrotic effects that ATRvD1 exerted in lung tissues, α-SMA expression was decreased, suggesting that myofibroblast differentiation was inhibited by ATRvD1. Turning to culture systems, we next showed that ATRvD1 impaired TGF-β-induced fibroblast differentiation into myofibroblast. After showing that ATRvD1 hampered extracellular vesicles (EVs) release in the supernatants from TGF-β-stimulated cultures of mouse macrophages, we verified that ATRvD1 also inhibited the release of EVs in the bronco-alveolar lavage (BAL) fluid of BLM-induced mice. Motivated by studies showing that BLM-induced lung fibrosis is linked to angiogenesis, we asked whether ATRvD1 could blunt BLM-induced angiogenesis in the hamster cheek pouch model (HCP). Indeed, our intravital microscopy studies confirmed that ATRvD1 abrogates BLM-induced angiogenesis. Collectively, our findings suggest that treatment of pulmonary fibrosis patients with ATRvD1 deserves to be explored as a therapeutic option in the clinical setting.
Keywords: ATRvD1; angiogenesis; fibrosis; inflammation; lung; macrophages; microparticles; tissue repair.
Copyright © 2023 Guilherme, Silva, Waclawiack, Fraga-Junior, Nogueira, Pecli, Araújo-Silva, Magalhães, Lemos, Bulant, Blanco, Serra, Svensjö, Scharfstein, Moraes, Canetti and Benjamim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATRvD1 Attenuates Renal Tubulointerstitial Injury Induced by Albumin Overload in Sepsis-Surviving Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 27;22(21):11634. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111634. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769064 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of andrographolide on the concentration of cytokines in BALF and the expressions of type I and III collagen mRNA in lung tissue in bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Jul;27(7):725-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21722520 Chinese.
-
Sulforaphane attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Apr 2;19(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40360-018-0204-7. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29609658 Free PMC article.
-
Grape seed extract ameliorates bleomycin-induced mouse pulmonary fibrosis.Toxicol Lett. 2017 May 5;273:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.03.012. Epub 2017 Mar 12. Toxicol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28300665
-
Asiatic acid ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin (BLM) via suppressing pro-fibrotic and inflammatory signaling pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 May;89:1297-1309. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.005. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28320097
Cited by
-
Resolvin D1 improves bleomycin-induced alveolar maturation arrest in newborn rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 5;15(1):28554. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12739-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40764724 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue factor targeting peptide enhances nanoparticle binding and delivery of a synthetic specialized pro-resolving lipid mediator to injured arteries.JVS Vasc Sci. 2023 Sep 26;4:100126. doi: 10.1016/j.jvssci.2023.100126. eCollection 2023. JVS Vasc Sci. 2023. PMID: 38045567 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a role for specialized pro-resolving mediators in pulmonary fibrosis?Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Jul;247:108460. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108460. Epub 2023 May 26. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37244406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

