Roles and therapeutic implications of m6A modification in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 36960074
- PMCID: PMC10028070
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1132601
Roles and therapeutic implications of m6A modification in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
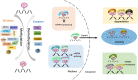
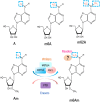
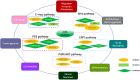
Recent studies have demonstrated that N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant, dynamic, and reversible epigenetic RNA modification in eukaryotes, is regulated by a series of enzymes, including methyltransferases (writers), demethylases (erasers), and m6A recognition proteins (readers). Aberrant regulation of m6A modification is pivotal for tumorigenesis, progression, invasion, metastasis, and apoptosis of malignant tumors. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has revolutionized cancer treatment, as recognized by the 2018 Nobel Prize in Medicine and Physiology. However, not all cancer patients response to ICI therapy, which is thought to be the result of intricate immune escape mechanisms. Recently, numerous studies have suggested a novel role for m6A epigenetic modification in the regulation of tumor immune evasion. Herein, we review the relevant mechanisms of m6A regulators in regulating various key signaling pathways in cancer biology and how m6A epigenetic modifications regulate the expression of immune checkpoints, opening a new window to understand the roles and mechanisms of m6A epigenetic modifications in regulating tumor immune evasion. In addition, we highlight the prospects and development directions of future combined immunotherapy strategies based on m6A modification targeting, providing directions for promoting the treatment outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Keywords: cancer; immune checkpoints; immunotherapy; m6A modification; m6A-regulator inhibitors.
Copyright © 2023 Pan, Huang, Deng and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
m6A epitranscriptomic modification in hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 17;16:1538658. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1538658. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40034695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The implications of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in esophageal carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Oct;50(10):8691-8703. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08575-2. Epub 2023 Aug 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37598390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research advances of N6-methyladenosine in diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Sep;36(9):e24611. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24611. Epub 2022 Jul 15. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35837987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting N6-methyladenosine RNA modification combined with immune checkpoint Inhibitors: A new approach for cancer therapy.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Sep 15;20:5150-5161. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.09.017. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36187919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Advances in the Roles of N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Ovarian Cancer.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241256819. doi: 10.1177/10732748241256819. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 38755968 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bibliometric analysis and visualization of the research on the relationship between RNA methylation and immune cell infiltration in tumors.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 12;15:1477828. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1477828. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39726589 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of RNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Apr 2;22(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01595-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38566136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Insights into Breast Cancer in Northeastern Mexico: Unveiling Gene-Environment Interactions and Their Links to Obesity and Metabolic Diseases.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 14;17(6):982. doi: 10.3390/cancers17060982. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149317 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of m6 A-regulated ferroptosis biomarkers for prognosis in laryngeal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Apr 14;25(1):694. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14134-8. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40229748 Free PMC article.
-
High‑dose sodium propionate contributes to tumor immune escape through the IGF2BP3/PD‑L1 axis in colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2025 Apr 16;29(6):303. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15049. eCollection 2025 Jun. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40291473 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

