Exploring the target and molecular mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus in the treatment of vascular cognitive impairment based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 36961195
- PMCID: PMC10036060
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033063
Exploring the target and molecular mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus in the treatment of vascular cognitive impairment based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
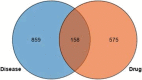
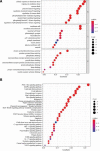
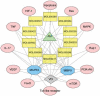
Astragalus membranaceus (AM) is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine extensively utilized in vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) treatment. However, due to the complex components of AM, its exact molecular mechanism remains unclear. Therefore, this study investigated the target and molecular mechanism of AM to treat VCI based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Firstly, the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform, STITCH, and SwissTargetPrediction were utilized to gather the primary active ingredients of AM. The potential therapeutic targets of VCI were collected through GeneCards, OMIM, and DisGeNET databases. Secondly, the protein-protein interaction network was built using the STRING database. The enrichment analysis of gene ontology and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome pathways was carried out in the R language. Finally, The network topology calculation of Cytoscape software was combined with module analysis to predict the binding properties of its active ingredients and targets. Twenty effective compounds and 733 targets were screened from AM, among which 158 targets were seen as possible targets of AM to treat VCI. MAPK3 and MMP9 were the critical targets of AM intervention in VCI. The crucial pathways include PI3K/Akt, MAPK, Rap1, and Ras signaling pathways. Besides, calycosin and quercetin might be the potential active compounds of AM for VCI treatment. AM intervenes in VCI through a multi-ingredient, multi-target, and multi-pathway coordination mechanism. These findings provide a foundation for a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms by which AM is effective in treating VCI.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking-Based Investigation of Potential Targets of Astragalus membranaceus and Angelica sinensis Compound Acting on Spinal Cord Injury.Dis Markers. 2022 Sep 15;2022:2141882. doi: 10.1155/2022/2141882. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. Retraction in: Dis Markers. 2023 Jul 26;2023:9824032. doi: 10.1155/2023/9824032. PMID: 36157206 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Anticancer Effect of Active Component of Astragalus Membranaceus Combined with Olaparib on Ovarian Cancer Predicted by Network-Based Pharmacology.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Nov;195(11):6994-7020. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04462-5. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36976504
-
Integration of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology reveals the mechanism of the herbal pairing of Codonopsis Pilosula (Franch.) Nannf and Astragalus Membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge on chronic heart failure.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jul;10(7):7942-7959. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1469. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34353081
-
Network pharmacology-based identification of miRNA expression of Astragalus membranaceus in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Feb 4;101(5):e28747. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028747. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35119030 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the molecular mechanism of Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan decoction for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Mar 24;102(12):e33210. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033210. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36961137 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emodin influences pyroptosis-related Caspase 1-GSDMD axis alleviated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 3;15(1):19397. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04863-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40461604 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent Functions of Rap1A and Rap1B in Endothelial Biology and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 4;26(11):5372. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115372. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropharmacological effects of calycosin: a translational review of molecular mechanisms and therapeutic applications.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 16. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04154-3. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40237798 Review.
References
-
- An XL, Li CL. Analysis of risk factors for vascular cognitive impairment in patients with cerebral infarction. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;71:673–7. - PubMed
-
- Smith EE. Clinical presentations and epidemiology of vascular dementia. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017;131:1059–68. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese V, Giordano J, Signorile A, et al. . Major pathogenic mechanisms in vascular dementia: roles of cellular stress response and hormesis in neuroprotection. J Neurosci Res. 2016;94:1588–603. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Wang Q, He Y, et al. . Astragaloside IV suppresses migration and invasion of TGF-β1-induced human hepatoma HuH-7 cells by regulating Nrf2/HO-1 and TGF-β1/Smad3 pathways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022;395:397–405. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

