Trauma Across the Life Span and Multisystem Morbidity in Women With HIV
- PMID: 36961349
- PMCID: PMC10450638
- DOI: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000001192
Trauma Across the Life Span and Multisystem Morbidity in Women With HIV
Abstract
Objective: Sexual and physical abuse are highly prevalent among women living with HIV (WLWH) and are risk factors for the development of mental health and substance use disorders (MHDs, SUDs), and cognitive and medical comorbidities. We examined empirically derived patterns of trauma, MHD, and SUD, and associations with later cognitive and health outcomes.
Methods: A total of 1027 WLWH (average age = 48.6 years) in the Women's Interagency HIV Study completed the World Mental Health Composite International Diagnostic Interview from 2010 to 2013 to identify MHDs, SUDs, and age at onset of sexual and physical abuse. Then, cognitive impairment, cardiovascular/metabolic conditions, and HIV disease outcomes were assessed for up to 8.8 years. Latent class analysis identified patterns of co-occurring trauma, MHDs, and/or SUDs. Generalized estimating equations determined associations between these patterns and midlife cognitive and medical outcomes.
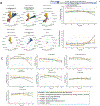
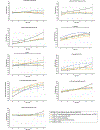
Results: Six distinct profiles emerged: no/negligible sexual/physical trauma, MHD, or SUD (39%); preadolescent/adolescent sexual trauma with anxiety and SUD (22%); SUD only (16%); MHD + SUD only (12%); early childhood sexual/physical trauma only (6%); and early childhood sexual/physical trauma with later MHD + SUD (4%). Profiles including early childhood trauma had the largest number of midlife conditions (i.e., cognitive, cardiovascular, HIV-related). Preadolescent/adolescent sexual trauma with anxiety and SUD predicted both global and domain-specific cognitive declines. Only SUD without trauma predicted lower CD4, whereas childhood trauma with MHD + SUD predicted increased CD8.
Conclusions: WLWH have complex multisystem profiles of abuse, MHD, and/or SUD that predict midlife cognitive, metabolic/cardiovascular, and HIV outcomes. Understanding the interplay between these factors over time can identify risks and personalize preventative and treatment interventions.
Copyright © 2023 by the American Psychosomatic Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- CDC. HIV and Women. 2020.
-
- Machtinger EL, Wilson TC, Haberer JE, Weiss DS. Psychological trauma and PTSD in HIV-positive women: a meta-analysis. AIDS Behav. [Meta-Analysis Review]. 2012;16:2091–100. - PubMed
-
- Knipscheer J, Sleijpen M, Frank L, de Graaf R, Kleber R, Ten Have M, Duckers M. Prevalence of Potentially Traumatic Events, Other Life Events and Subsequent Reactions Indicative for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in the Netherlands: A General Population Study Based on the Trauma Screening Questionnaire. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frans O, Rimmo PA, Aberg L, Fredrikson M. Trauma exposure and post-traumatic stress disorder in the general population. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2005;111:291–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 MH075673/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146192/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146193/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH089830/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 MH123290/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146240/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH098798/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146203/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

