Unraveling the roles of cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons
- PMID: 36961498
- PMCID: PMC10038656
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.87054
Unraveling the roles of cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons
Abstract
Sensory neurons previously shown to optimize speed and balance in fish by providing information about the curvature of the spine show similar morphology and connectivity in mice.
Keywords: PKD2L1; cerebrospinal fluid; cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neuron; interoception; locomotion; mechanosensation; mouse; neural circuit; neuroscience; proprioception; spinal cord.
© 2023, Wyart.
Conflict of interest statement
CW No competing interests declared
Figures
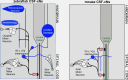
Comment on
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.83108
References
-
- Böhm UL, Prendergast A, Djenoune L, Nunes Figueiredo S, Gomez J, Stokes C, Kaiser S, Suster M, Kawakami K, Charpentier M, Concordet JP, Rio JP, Del Bene F, Wyart C. CSF-contacting neurons regulate locomotion by relaying mechanical stimuli to spinal circuits. Nature Communications. 2016;7:10866. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10866. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Djenoune L, Khabou H, Joubert F, Quan FB, Nunes Figueiredo S, Bodineau L, Del Bene F, Burcklé C, Tostivint H, Wyart C. Investigation of spinal cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons expressing PKD2L1: evidence for a conserved system from fish to primates. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy. 2014;8:26. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2014.00026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

