A Randomized, Open-Label, Multiple-Dose, Parallel-Arm, Pivotal Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Aripiprazole 2-Month Long-Acting Injectable in Adults With Schizophrenia or Bipolar I Disorder
- PMID: 36961650
- PMCID: PMC10126081
- DOI: 10.1007/s40263-023-00996-8
A Randomized, Open-Label, Multiple-Dose, Parallel-Arm, Pivotal Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Aripiprazole 2-Month Long-Acting Injectable in Adults With Schizophrenia or Bipolar I Disorder
Abstract
Background: Aripiprazole 2-month ready-to-use 960 mg (Ari 2MRTU 960) is a new long-acting injectable antipsychotic formulation for gluteal administration every 2 months, currently being investigated for the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar I disorder (BP-I). The objectives of this trial were to evaluate the safety and tolerability of Ari 2MRTU 960, and the similarity of aripiprazole plasma concentrations following administration of Ari 2MRTU 960 or aripiprazole once-monthly 400 mg (AOM 400), in adults with schizophrenia or BP-I.
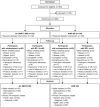
Methods: This was a 32-week open-label study. Eligible participants were randomized 1:1 to receive Ari 2MRTU 960 every 56 ± 2 days (four injections scheduled) or AOM 400 every 28 ± 2 days (eight injections scheduled). Participants received overlapping oral antipsychotic treatment with the first administration of study drug (there was no oral overlap for participants stabilized on AOM 400). Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics (PK) were evaluated throughout the study. Primary safety endpoints included reported adverse events, injection site reactions, and extrapyramidal symptoms. Primary PK endpoints were plasma concentration of aripiprazole 56 days after the fourth dose of Ari 2MRTU 960 and 28 days after the eighth dose of AOM 400, and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) from Day 0 to 56 postdose after the fourth dose of Ari 2MRTU 960, or AUC from Day 0 to 28 after the seventh and eighth doses of AOM 400.
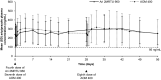
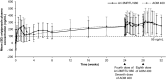
Results: Of the 266 participants enrolled (schizophrenia, n = 185; BP-I, n = 81), 132 were randomized to receive Ari 2MRTU 960 and 134 were randomized to receive AOM 400. The majority (66.2%) of participants were male; 72.9% were Black or African American, and mean age was 47.3 years; demographic characteristics and baseline disease characteristics were generally well balanced between groups. Study completion rate was 77.3% in the Ari 2MRTU 960 group and 68.7% in the AOM 400 group. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) was similar between Ari 2MRTU 960 (71.2%) and AOM 400 (70.9%). The most frequently reported TEAEs were increased weight (Ari 2MRTU 960: 22.7%; AOM 400: 20.9%) and injection-site pain (Ari 2MRTU 960: 18.2%; AOM 400: 9.0%). The geometric means ratio (GMR) of aripiprazole plasma concentrations on the last day following the final dosing for Ari 2MRTU 960 versus AOM 400 was 1.011 (90% confidence interval [CI] 0.893-1.145), and the GMR of aripiprazole plasma exposure (area under the concentration-time curve) over the fourth Ari 2MRTU 960 dosing interval versus the seventh and eighth AOM 400 dosing intervals was 1.006 (90% CI 0.851-1.190).
Conclusions: Ari 2MRTU 960 was generally well tolerated in adults with schizophrenia or BP-I, with a safety profile comparable with that of AOM 400, and aripiprazole exposure equivalent to that with AOM 400 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04030143, registered on 23 July 2019).
Plain language summary
Aripiprazole is a medication used to treat psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder (BP-I) that can be taken orally or injected into the muscle. Aripiprazole once-monthly 400 mg (AOM 400) is a long-acting injectable formulation administered every 28 days, used in the treatment of schizophrenia or BP-I. A new 2-month ready-to-use formulation containing 960 mg of aripiprazole (Ari 2MRTU 960) is currently being investigated for the treatment of schizophrenia or BP-I. This 32-week study compared Ari 2MRTU 960 with AOM 400 in adults with schizophrenia or BP-I stabilized on their current medication. Study participants were randomly assigned to receive either Ari 2MRTU 960 every 56 ± 2 days (four injections scheduled in total) or AOM 400 every 28 ± 2 days (eight injections scheduled in total). Safety, tolerability, and concentration of aripiprazole in the blood were evaluated throughout the study. The incidence of adverse events emerging during the treatment period was similar between Ari 2MRTU 960 and AOM 400 (71.2% and 70.9%, respectively), with the most frequently reported events being increased weight (Ari 2MRTU 960: 22.7%; AOM 400: 20.9%) and injection-site pain (Ari 2MRTU 960: 18.2%; AOM 400: 9.0%). At the end of the study, aripiprazole concentrations were similar between treatment groups, based on the reported pharmacokinetic parameters. Participants remained clinically stable throughout the study. Ari 2MRTU 960 was generally well tolerated in adults with schizophrenia or BP-I.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Matthew Harlin, Jessica Madera-McDonough, Michael Jan, Na Jin, and Suzanne Watkin are full-time employees of Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization Inc. Murat Yildirim, Pedro Such, and Frank Larsen are full-time employees of H. Lundbeck A/S.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Arlington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2021. https://psychiatryonline.org/doi/pdf/10.1176/appi.books.9780890424841. Accessed 22 Jun 2022. - DOI
-
- Vázquez GH, Holtzman JN, Lolich M, Ketter TA, Baldessarini RJ. Recurrence rates in bipolar disorder: systematic comparison of long-term prospective, naturalistic studies versus randomized controlled trials. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;25(10):1501–1512. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.07.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

