Factors associated with pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage: A systematic review
- PMID: 36962225
- PMCID: PMC10021834
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0000327
Factors associated with pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage: A systematic review
Abstract
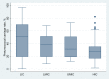
Pneumococcal disease is a major contributor to global childhood morbidity and mortality and is more common in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) than in high-income countries. Pneumococcal carriage is a prerequisite for pneumococcal disease. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine reduces vaccine-type carriage and disease. However, pneumococcal carriage and disease persist, and it is important to identify other potentially modifiable factors associated with pneumococcal carriage and determine if risk factors differ between low, middle, and high-income countries. This information may help inform pneumococcal disease prevention programs. This systematic literature review describes factors associated with pneumococcal carriage stratified by country income status and summarises pneumococcal carriage rates for included studies. We undertook a systematic search of English-language pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage studies up to 30th June 2021. Peer-reviewed studies reporting factors associated with overall pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage in healthy, community-based study populations were eligible for inclusion. Two researchers independently reviewed studies to determine eligibility. Results are presented as narrative summaries. This review is registered with PROSPERO, CRD42020186914. Eighty-two studies were included, and 46 (56%) were conducted in LMICs. There was heterogeneity in the factors assessed in each study. Factors positively associated with pneumococcal carriage in all income classification were young age, ethnicity, symptoms of respiratory tract infection, childcare attendance, living with young children, poverty, exposure to smoke, season, and co-colonisation with other pathogens. Breastfeeding and antibiotic use were protective against carriage in all income classifications. Median (interquartile range) pneumococcal carriage rates differed by income classification, ranging from 51% (19.3-70.2%), 38.5% (19.3-51.6%), 31.5% (19.0-51.0%), 28.5% (16.8-35.4%), (P = 0.005) in low-, lower-middle, upper-middle, and high-income classifications, respectively. Our findings suggest that where measured, factors associated with pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage are similar across income classifications, despite the highest pneumococcal carriage rates being in low-income classifications. Reducing viral transmission through vaccination and public health interventions to address social determinants of health would play an important role.
Copyright: © 2022 Neal et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Troeger C, Forouzanfar M, Rao PC, Khalil I, Brown A, Swartz S, et al. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory tract infections in 195 countries: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17(11):1133–61. Epub 08/23. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30396-1 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wahl B, O’Brien KL, Greenbaum A, Majumder A, Liu L, Chu Y, et al. Burden of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in children in the era of conjugate vaccines: global, regional, and national estimates for 2000–15. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6(7):e744–e57. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30247-X . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
