The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the uptake of routine maternal and infant vaccines globally: A systematic review
- PMID: 36962643
- PMCID: PMC10022285
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0000628
The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the uptake of routine maternal and infant vaccines globally: A systematic review
Abstract
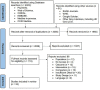
Maintaining routine vaccination coverage is essential to avoid outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases. We aimed to understand the international impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on routine vaccination in pregnant women and children aged 0-5-years-old. A systematic review of quantitative and mixed methods studies exploring changes in vaccination coverage, vaccination services, and vaccine confidence since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic was conducted. MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINHAL, PsychINFO, Web of Science, Google Scholar, World Health Organisation, UK Government Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (including EU and US equivalents), and SAGE Journals were searched between 15-17th June 2021. Selected studies included pregnant women, health professionals, and/or infants aged 0-5-years-old including their parents (population); reported on the Covid-19 pandemic (exposure); presented comparisons with pre-COVID-19 pandemic period (comparator) and reported changes in routine maternal and infant vaccination coverage, services, and confidence (outcomes). Sources published only in non-English language were excluded. The Newcastle Ottawa Scale was used to assess study quality and risk of bias (ROB), and a narrative synthesis was undertaken. This review has been registered with PROSPERO (CRD42021262449). 30 studies were included in the review; data from 20 high-income countries (HICs), seven low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), and three regional studies (groups of countries). 18 studies had a low ROB, 12 had a higher risk, however both low and high ROB studies showed similar results. Two studies meeting the inclusion criteria discussed changes in routine vaccinations for pregnant women while 29 studies discussed infants. Both groups experienced declines in vaccination coverage (up to -79%) with larger disruptions in the accessibility and delivery of vaccination services reported within LMICs compared to HICs. Changes in vaccine confidence remained unclear. The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in decreased vaccine coverage and reduced routine vaccination services for pregnant women and infants, impacts on vaccine confidence requires more research.
Copyright: © 2022 Yunusa et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Vaccines and immunization [Internet]. [cited 2022 Mar 30]. Available from: https://www.who.int/health-topics/vaccines-and-immunization#tab=tab_1
-
- Whooping cough vaccination in pregnancy—NHS [Internet]. [cited 2022 Mar 30]. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/whooping-cough-vaccination/
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard | WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard With Vaccination Data [Internet]. [cited 2022 Mar 30]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources