Correlates of protection against COVID-19 infection and intensity of symptomatic disease in vaccinated individuals exposed to SARS-CoV-2 in households in Israel (ICoFS): a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 36963419
- PMCID: PMC10030121
- DOI: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00012-5
Correlates of protection against COVID-19 infection and intensity of symptomatic disease in vaccinated individuals exposed to SARS-CoV-2 in households in Israel (ICoFS): a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Identifying COVID-19 correlates of protection and immunity thresholds is important for policy makers and vaccine development. We aimed to identify correlates of protection of BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccination against COVID-19.
Methods: In this prospective cohort study, households within a radius of 40 km of the Sheba Medical Center in Israel in which a new SARS-CoV-2 infection (defined as the index case) was detected within the previous 24 h were approached between July 25 and Nov 15, 2021. We included adults (aged >18 years) who had received one or two vaccine doses, had an initial negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR and no previous infection reported, and had a valid IgG and neutralising antibody result. The exposure of interest was baseline immune status, including IgG antibody concentration, neutralising antibody titre, and T-cell activation. The outcomes of interest were PCR-positive SARS-CoV-2 infection between day 2 and day 21 of follow-up and intensity of disease symptoms (self-reported via a telephone questionnaire) among participants who had a confirmed infection. Multivariable logistic and ordered logit ordinal regressions were used for the adjusted analysis. To identify immunological thresholds for clinical protection, we estimated the conditional probability of infection and moderate or severe disease for individuals with pre-exposure IgG and neutralising antibody concentrations above each value observed in the study data.
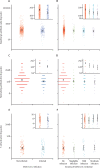
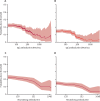
Findings: From 16 675 detected index cases in the study region, 5718 household members agreed to participate, 1461 of whom were eligible to be included in our study. 333 (22·8%) of 1461 household members who were not infected with SARS-CoV-2 at baseline were infected within 21 days of follow-up. The baseline (pre-exposure) IgG and neutralising antibodies were higher in participants who remained uninfected than in those who became infected (geometric mean IgG antibody concentration 168·2 binding antibody units [BAU] per mL [95% CI 158·3-178·7] vs 130·5 BAU/mL [118·3-143·8] and geometric mean neutralising antibody titre 197·5 [181·9-214·4] vs 136 ·7 [120·3-155·4]). Increasing IgG and neutralising antibody concentrations were also significantly associated with a reduced probability of increasing disease severity. Odds of infection were significantly reduced each time baseline IgG antibody concentration increased by a factor of ten (odds ratio [OR] 0·43 [95% CI 0·26-0·70]) and each time baseline neutralising antibody titre increased by a factor of two (0·82 [0·74-0·92]). In our cohort, the probability of infection if IgG antibody concentrations were higher than 500 BAU/mL was 11% and the probability of moderate disease severity was 1%; the probability of infection if neutralising antibody titres were above or equal to 1024 was 8% and the probability of moderate disease severity was 2%. T-cell activation rates were not significantly associated with reduced probability of infection (OR 1·04, 95% CI 0·83-1·30).
Interpretation: Both IgG and neutralising antibodies are correlates of protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Our data suggest that IgG concentrations higher than 500 BAU/mL and neutralising antibody titres of 1024 or more are thresholds for immunological protection from SARS-CoV-2 delta variant infection. Potentially, updated protective thresholds against emerging variants of concern could be calculated, which could support decision makers on administration of new vaccination strategies and on the optimal period between vaccine doses.
Funding: Israeli Ministry of Health.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests GRY served as a member of an advisory board for Moderna, and received consulting fees from Medison and speaking fees from Teva, MSD, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Medison. YL received a grant from Pfizer outside the submitted work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine and correlates of humoral immune responses and dynamics: a prospective, single-centre, longitudinal cohort study in health-care workers.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Sep;9(9):999-1009. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00220-4. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 34224675 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 lateral flow IgG seropositivity and serum neutralising antibody responses after primary and booster vaccinations in Chile: a cross-sectional study.Lancet Microbe. 2023 Mar;4(3):e149-e158. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(22)00290-7. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Lancet Microbe. 2023. PMID: 36716754 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody and T-cell responses 1 year after infection in people recovered from COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study.Lancet Microbe. 2022 May;3(5):e348-e356. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(22)00036-2. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Lancet Microbe. 2022. PMID: 35345417 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in acute infection and convalescence: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jul 8;15(7):e0009551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009551. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34237072 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 31;15(12):e0244126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244126. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33382764 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 shedding and evolution in immunocompromised hosts during the Omicron period: a multicenter prospective analysis.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 24:2023.08.22.23294416. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.22.23294416. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Lancet Microbe. 2024 Mar;5(3):e235-e246. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00336-1. PMID: 37662226 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Vaccine Responses in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: From the Immune System to the Gut Microbiota.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Mar 23;12(4):349. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12040349. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 point-of-care tests can identify low-antibody individuals: In-depth immunoanalysis of boosting benefits in a healthy cohort.Sci Adv. 2024 Jun 14;10(24):eadi1379. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi1379. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38865463 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric humoral immune responses and infection risk after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and two-dose vaccination during SARS-CoV-2 omicron BA.5 and BN.1 variants predominance in South Korea.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 20;14:1306604. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1306604. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38193075 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and laboratory considerations: determining an antibody-based composite correlate of risk for reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 or severe COVID-19.Front Public Health. 2023 Dec 28;11:1290402. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1290402. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38222091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haas EJ, Angulo FJ, McLaughlin JM, et al. Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: an observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet. 2021;397:1819–1829. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

