Older patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma: Survival and prognostication across 20 U.S. cancer centers
- PMID: 36965007
- PMCID: PMC10979647
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.26919
Older patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma: Survival and prognostication across 20 U.S. cancer centers
Abstract
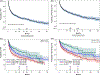
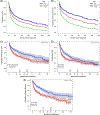
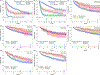
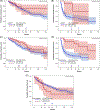
There is a paucity of large-scale data delineating outcomes and prognostication of older patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). We retrospectively analyzed 539 newly-diagnosed PCNSL patients ages ≥60 years across 20 U.S. academic centers. The median age was 70 years (range 60-88); at least one geriatric syndrome was present in 46%; the median Cumulative Index Ratings Scale-Geriatrics (CIRS-G) score was 6 (range, 0-27); and 36% had impairment in activities of daily living (ADL). The most common induction regimens were high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX) ± rituximab; methotrexate, temozolomide, rituximab (MTR); and rituximab, methotrexate, procarbazine, vincristine (R-MPV). Overall, 70% of patients achieved remission, with 14% undergoing consolidative autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) and 24% receiving maintenance. With 58-month median follow-up, median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 17 months (95% CI 13-22 months) and 43 months (95% CI 31-56 months), respectively. Three-year PFS and OS were highest with MTR (55% and 74%, respectively). With single-agent methotrexate ± rituximab, 3-year PFS and OS were 30% (p = .0002) and 47% (p = .0072). On multivariate analysis, increasing age at diagnosis and Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) was associated with inferior PFS; age, hypoalbuminemia, higher CIRS-G score, and ECOG PS adversely affected OS. Among patients receiving maintenance, 3-year PFS was 65% versus 45% without maintenance (p = 0.02), with 3-year OS of 84% versus 61%, respectively (p = .0003). Altogether, outcomes in older PCNSL patients appeared optimized with HD-MTX combination induction regimens and maintenance therapy. Furthermore, several prognostic factors, including geriatric measures, were associated with inferior outcomes.
© 2023 The Authors. American Journal of Hematology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
Veronika Bachanova: Gamida Cell: membership on Board of Directors or advisory committee and Research Funding.
David A. Bond: Kite/Gilead: Consultancy; Sea Gen: Consultancy. Stephen Spurgeon: Velos Bio: Consultancy and Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy and Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy and Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; BeiGene: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Ionis: Research Funding; Merck & Co: Research Funding;
Reem Karmali: Kite/Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding and Speakers Bureau; BMS/Celgene/Juno: Consultancy and Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; BeiGene: Consultancy and Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Speakers Bureau; Morphosys: Consultancy and Speakers Bureau; Epizyme: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Janssen/Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; EUSA: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy.
Peter Martin: ADCT: Consultancy.
Sonali M. Smith: Portola: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; Gilead/Kite: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Morphosys: Consultancy; Adaptive: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; TGTX: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy.
Brad Kahl: AbbVie: Research Funding; ADCT: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; BeiGene: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy; Adaptive: Consultancy; ADCT: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; BeiGene: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy; MEI: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Teva: Consultancy.
Andrew Evens: Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Research to Practice: Honoraria; Verastem: Consultancy, Honoraria; Affimed: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Other: DMC; Bayer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding.
Figures
References
-
- Siegal T, Bairey O. Primary CNS lymphoma in the elderly: the challenge. Acta Haematol. 2019;141(3):138–145. - PubMed
-
- Ferreri AJM, Holdhoff M, Nayak L, Rubenstein JL. Evolving treatments for primary central nervous system lymphoma. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2019;39:454–466. - PubMed
-
- Shah GD, Yahalom J, Correa DD, et al. Combined immunochemotherapy with reduced whole-brain radiotherapy for newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(30):4730–4735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
