Biochemical study of the effect of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome versus L-Dopa in experimentally induced Parkinson's disease in rats
- PMID: 36966421
- PMCID: PMC10627934
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-023-04700-8
Biochemical study of the effect of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome versus L-Dopa in experimentally induced Parkinson's disease in rats
Abstract
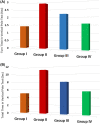
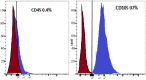
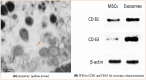
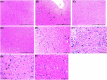
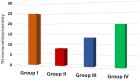
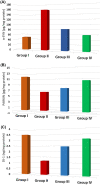
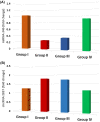
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic and ongoing neurological condition. Unfortunately, as the dopaminergic terminals continue to deteriorate, the effectiveness of anti-Parkinson therapy decreases. This study aimed to examine the effects of BM-MSCs-derived exosomes in rats induced with Parkinson's disease. The goal was to determine their potential for neurogenic repair and functional restoration. Forty male albino rats were divided into four groups: control (group I), PD (group II), PD-L-Dopa (group III), and PD-exosome (group IV). Motor tests, histopathological examinations, and immunohistochemistry for tyrosine hydroxylase were performed on brain tissue. The levels of α-synuclein, DJ-1, PARKIN, circRNA.2837, and microRNA-34b were measured in brain homogenates. Rotenone induced motor deficits and neuronal alterations. Groups (III) and (IV) showed improvement in motor function, histopathology, α-synuclein, PARKIN, and DJ-1 compared to group (II). Group (IV) showed improvement in microRNA-34b and circRNA.2837 compared to groups (III) and (II). MSC-derived exosomes showed a greater suppression of neurodegenerative disease (ND) compared to L-Dopa in Parkinson's patients.
Keywords: DJ-1; Exosome; PARKIN; Parkinson’ disease (PD); circRNA.2837; microRNA-34b.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

