Persistent SARS-CoV-2-specific immune defects in kidney transplant recipients following third mRNA vaccine dose
- PMID: 36966905
- PMCID: PMC10037915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajt.2023.03.014
Persistent SARS-CoV-2-specific immune defects in kidney transplant recipients following third mRNA vaccine dose
Abstract
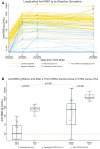
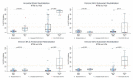
Kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) show poorer response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination, yet response patterns and mechanistic drivers following third doses are ill-defined. We administered third monovalent mRNA vaccines to n = 81 KTRs with negative or low-titer anti-receptor binding domain (RBD) antibody (n = 39 anti-RBDNEG; n = 42 anti-RBDLO), compared with healthy controls (HCs, n = 19), measuring anti-RBD, Omicron neutralization, spike-specific CD8+%, and SARS-CoV-2-reactive T cell receptor (TCR) repertoires. By day 30, 44% anti-RBDNEG remained seronegative; 5% KTRs developed BA.5 neutralization (vs 68% HCs, P < .001). Day 30 spike-specific CD8+% was negative in 91% KTRs (vs 20% HCs; P = .07), without correlation to anti-RBD (rs = 0.17). Day 30 SARS-CoV-2-reactive TCR repertoires were detected in 52% KTRs vs 74% HCs (P = .11). Spike-specific CD4+ TCR expansion was similar between KTRs and HCs, yet KTR CD8+ TCR depth was 7.6-fold lower (P = .001). Global negative response was seen in 7% KTRs, associated with high-dose MMF (P = .037); 44% showed global positive response. Of the KTRs, 16% experienced breakthrough infections, with 2 hospitalizations; prebreakthrough variant neutralization was poor. Absent neutralizing and CD8+ responses in KTRs indicate vulnerability to COVID-19 despite 3-dose mRNA vaccination. Lack of neutralization despite CD4+ expansion suggests B cell dysfunction and/or ineffective T cell help. Development of more effective KTR vaccine strategies is critical. (NCT04969263).
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; antibody; clinical trial; immunogenicity; kidney transplant; vaccination.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Rincon-Arevalo H., Choi M., Stefanski A.L., et al. Impaired humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients and dialysis patients. Sci Immunol. 2021;6(60) - PubMed
-
- Gilbert P.B., Donis R.O., Koup R.A., Fong Y., Plotkin S.A., Follmann D. A Covid-19 milestone attained – a correlate of protection for vaccines. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(24):2203–2206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

