Wnt regulation of hematopoietic stem cell development and disease
- PMID: 36967197
- PMCID: PMC11104846
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2022.12.001
Wnt regulation of hematopoietic stem cell development and disease
Abstract
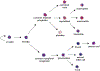
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are multipotent stem cells that give rise to all cells of the blood and most immune cells. Due to their capacity for unlimited self-renewal, long-term HSCs replenish the blood and immune cells of an organism throughout its life. HSC development, maintenance, and differentiation are all tightly regulated by cell signaling pathways, including the Wnt pathway. Wnt signaling is initiated extracellularly by secreted ligands which bind to cell surface receptors and give rise to several different downstream signaling cascades. These are classically categorized either β-catenin dependent (BCD) or β-catenin independent (BCI) signaling, depending on their reliance on the β-catenin transcriptional activator. HSC development, homeostasis, and differentiation is influenced by both BCD and BCI, with a high degree of sensitivity to the timing and dosage of Wnt signaling. Importantly, dysregulated Wnt signals can result in hematological malignancies such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma. Here, we review how Wnt signaling impacts HSCs during development and in disease.
Keywords: Hematopoietic stem cells; Leukemia; Lymphoma; Myeloma; Wnt.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

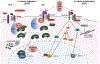
References
-
- Abrahamsson AE, Geron I, Gotlib J, Dao KH, Barroga CF, Newton IG, Giles FJ, Durocher J, Creusot RS, Karimi M, Jones C, Zehnder JL, Keating A, Negrin RS, Weissman IL, & Jamieson CH (2009). Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta missplicing contributes to leukemia stem cell generation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(10), 3925–3929. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akashi K, He X, Chen J, Iwasaki H, Niu C, Steenhard B, Zhang J, Haug J, & Li L (2003). Transcriptional accessibility for genes of multiple tissues and hematopoietic lineages is hierarchically controlled during early hematopoiesis. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology, 101(2), 383–389. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht LV, Tejeda-Munoz N, & De Robertis EM (2021). Cell Biology of Canonical Wnt Signaling. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 37, 369–389. - PubMed
-
- Austin TW, Solar GP, Ziegler FC, Liem L, & Matthews W (1997). A role for the Wnt gene family in hematopoiesis: expansion of multilineage progenitor cells. Blood, 89(10), 3624–3635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

