Immunotherapeutic approach to reduce senescent cells and alleviate senescence-associated secretory phenotype in mice
- PMID: 36967480
- PMCID: PMC10186597
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13806
Immunotherapeutic approach to reduce senescent cells and alleviate senescence-associated secretory phenotype in mice
Abstract
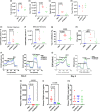
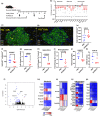
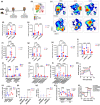
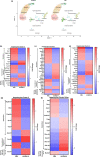
Accumulation of senescent cells (SNCs) with a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) has been implicated as a major source of chronic sterile inflammation leading to many age-related pathologies. Herein, we provide evidence that a bifunctional immunotherapeutic, HCW9218, with capabilities of neutralizing TGF-β and stimulating immune cells, can be safely administered systemically to reduce SNCs and alleviate SASP in mice. In the diabetic db/db mouse model, subcutaneous administration of HCW9218 reduced senescent islet β cells and SASP resulting in improved glucose tolerance, insulin resistance, and aging index. In naturally aged mice, subcutaneous administration of HCW9218 durably reduced the level of SNCs and SASP, leading to lower expression of pro-inflammatory genes in peripheral organs. HCW9218 treatment also reverted the pattern of key regulatory circadian gene expression in aged mice to levels observed in young mice and impacted genes associated with metabolism and fibrosis in the liver. Single-nucleus RNA Sequencing analysis further revealed that HCW9218 treatment differentially changed the transcriptomic landscape of hepatocyte subtypes involving metabolic, signaling, cell-cycle, and senescence-associated pathways in naturally aged mice. Long-term survival studies also showed that HCW9218 treatment improved physical performance without compromising the health span of naturally aged mice. Thus, HCW9218 represents a novel immunotherapeutic approach and a clinically promising new class of senotherapeutic agents targeting cellular senescence-associated diseases.
Keywords: aging; cellular immunology; circadian genes; immunotherapy; inflammation; physical performance; senescence; senescent cell reduction; senomorphic; type 2 diabetes.
© 2023 HCW Biologics Inc, Washington University School of Medicine and Nova Southeastern University. Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
HCW9218 is protected under US Patent No. 11,518, 972 and other pending patent applications. Unrelated to this work, MMB‐E and TAF are inventors on patent/patent applications (15/983,275; 62/963,971, and PCT/US2019/060005) licensed to Wugen, Inc. and held/submitted by Washington University that covers aspects of ML NK cell biology. This results in potential royalties to MMB‐E, TAF, and Washington University from Wugen, Inc. MMB‐E, TAF consults for and has equity in Wugen Inc. Unrelated to this work, JAF is an inventor on patent/patent application (WO 2019/152387, US 63/018,108) licensed to Kiadis, Inc. and held/submitted by Nationwide Children's Hospital on TGF‐β resistant, expanded NK cells. Unrelated to this work, JAF has a monoclonal antibody unrelated to the present work licensed to EMD Millipore. Unrelated to this work, CCC reports equity in Pionyr Immunotherapeutics. Unrelated to this work, TAF consults for Affimed (SAB) and advises (equity interest) Indapta and OrcaBio.
Figures


References
-
- Aguayo‐Mazzucato, C. , Andle, J. , Lee, T. B., Jr. , Midha, A. , Talemal, L. , Chipashvili, V. , Hollister‐Lock, J. , van Deursen, J. , Weir, G. , & Bonner‐Weir, S. (2019). Acceleration of beta cell aging determines diabetes and Senolysis improves disease outcomes. Cell Metabolism, 30, 129–142.e4. 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.05.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amor, C. , Feucht, J. , Leibold, J. , Ho, Y. J. , Zhu, C. , Alonso‐Curbelo, D. , Mansilla‐Soto, J. , Boyer, J. A. , Li, X. , Giavridis, T. , Kulick, A. , Houlihan, S. , Peerschke, E. , Friedman, S. L. , Ponomarev, V. , Piersigilli, A. , Sadelain, M. , & Lowe, S. W. (2020). Senolytic CAR T cells reverse senescence‐associated pathologies. Nature, 583, 127–132. 10.1038/s41586-020-2403-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker, D. J. , Childs, B. G. , Durik, M. , Wijers, M. E. , Sieben, C. J. , Zhong, J. , A. Saltness, R. , Jeganathan, K. B. , Verzosa, G. C. , Pezeshki, A. , Khazaie, K. , Miller, J. D. , & van Deursen, J. M. (2016). Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)‐positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature, 530, 184–189. 10.1038/nature16932 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

