Continuous Measurement of Lactate Concentration in Human Subjects through Direct Electron Transfer from Enzymes to Microneedle Electrodes
- PMID: 36967522
- PMCID: PMC10152478
- DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.2c02780
Continuous Measurement of Lactate Concentration in Human Subjects through Direct Electron Transfer from Enzymes to Microneedle Electrodes
Abstract
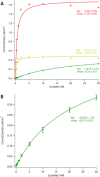
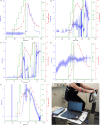
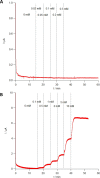
Microneedle lactate sensors may be used to continuously measure lactate concentration in the interstitial fluid in a minimally invasive and pain-free manner. First- and second-generation enzymatic sensors produce a redox-active product that is electrochemically sensed at the electrode surface. Direct electron transfer enzymes produce electrons directly as the product of enzymatic action; in this study, a direct electron transfer enzyme specific to lactate has been immobilized onto a microneedle surface to create lactate-sensing devices that function at low applied voltages (0.2 V). These devices have been validated in a small study of human volunteers; lactate concentrations were raised and lowered through physical exercise and subsequent rest. Lactazyme microneedle devices show good agreement with concurrently obtained and analyzed serum lactate levels.
Keywords: biosensor; continuous monitoring; direct electron transfer enzyme; in-human study; lactate; microneedles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): AEGC is the founder of a company, Continuous Diagnostics Ltd., involved in commercialisation of microneedle sensing devices. AKGF is the co-founder of a company, DirectSens GmbH, involved in commercialisation of enzyme-based sensor technology.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

