Assessment of Changes in Craniofacial Structures, Bite Force and Periodontal Status Following Fixed Functional Appliance Therapy
- PMID: 36967592
- PMCID: PMC10140664
- DOI: 10.4274/TurkJOrthod.2022.2021.0229
Assessment of Changes in Craniofacial Structures, Bite Force and Periodontal Status Following Fixed Functional Appliance Therapy
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine the effect of Forsus Fatigue Resistant Device (FRD) appliance on craniofacial structures, bite force and periodontal status in Class II malocclusion patients.
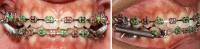
Methods: In this prospective interventional follow-up study, thirteen (13) Class II Division 1 patients in their post-adolescent age group with average age of 17.10 ± 1.63 year was treated with Forsus FRD. They were assessed for craniofacial changes, bite force and periodontal status at baseline, after alignment and leveling, after removal of FRD.
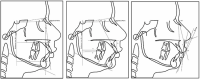
Results: Improvement in soft tissue profile was due to significant dentoalveolar changes. There were significant decreases in overjet, overbite, reference line to upper first molar, H angle (p<0.001) and significant increases in upper lip to E-line, reference line to lower molar and angular measurements like nasolabial angle, U1 to SN plane, Incisor Mandibular Plane Angle (p<0.001). The bite force was significantly decreased on the molar and the incisor region (p<0.001). A significant increase in plaque index (PI), gingival index (GI), probing pocket depth was noticed without any significant clinical attachment loss.
Conclusion: Class II correction with Forsus FRD appliance was mainly due to significant dentoalveolar changes. Skeletal changes were non-significant. A decrease in the bite force was found with FRD. The magnitude of bite force was more in males compared with females. The increase in GI, PI, pocket probing depth implies the necessity of oral hygiene and plaque control measures. However, there was no significant change in clinical attachment level.
Keywords: Class II Division I malocclusion; Forsus FRD; bite force; fixed functional appliance; gingival index; plaque index.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Alarashi M, Franchi L, Marinelli A, Defraia E. Morphometric analysis of the transverse dentoskeletal features of class II malocclusion in the mixed dentition. Angle Orthod. 2003;73(1):21–25. - PubMed
-
- McNamara JA Jr. Components of class II malocclusion in children 8-10 years of age. Angle Orthod. 1981;51(3):177–202. - PubMed
-
- McSherry PF, Bradley H. Class II correction-reducing patient compliance: a review of the available techniques. J Orthod. 2000;27(3):219–225. - PubMed
-
- Vogt W. The Forsus Fatigue Resistant Device. J Clin Orthod. 2006;40(6):368–377; quiz 358. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous