Effect of Bifidobacterium on osteoclasts: TNF-α/NF-κB inflammatory signal pathway-mediated mechanism
- PMID: 36967748
- PMCID: PMC10034056
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1109296
Effect of Bifidobacterium on osteoclasts: TNF-α/NF-κB inflammatory signal pathway-mediated mechanism
Abstract
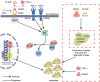
Osteoporosis is a systemic multifactorial bone disease characterized by low bone quality and density and bone microstructure damage, increasing bone fragility and fracture vulnerability. Increased osteoclast differentiation and activity are important factors contributing to bone loss, which is a common pathological manifestation of bone diseases such as osteoporosis. TNF-a/NF-κB is an inflammatory signaling pathway with a key regulatory role in regulating osteoclast formation, and the classical pathway RANKL/RANK/OPG assists osteoclast formation. Activation of this inflammatory pathway promotes the formation of osteoclasts and accelerates the process of osteoporosis. Recent studies and emerging evidence have consistently demonstrated the potential of probiotics to modulate bone health. Secretions of Bifidobacterium, a genus of probiotic bacteria in the phylum Actinobacteria, such as short-chain fatty acids, equol, and exopolysaccharides, have indicated beneficial effects on bone health. This review discusses the molecular mechanisms of the TNF-a/NF-κB inflammatory pathway in regulating osteoclast formation and describes the secretions produced by Bifidobacterium and their potential effects on bone health through this pathway, opening up new directions for future research.
Keywords: Bifidobacterium; NF-κB; TNF-α; inflammation; osteoclast.
Copyright © 2023 Wu, Yang, Wang, Chen, Han, Sun, Chen and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mosca L, Grady D, Barrett-Connor E, Collins P, Wenger N, Abramson BL, et al. . Effect of raloxifene on stroke and venous thromboembolism according to subgroups in postmenopausal women at increased risk of coronary heart disease. Stroke (2009) 40(1):147–55. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.518621 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

