MXene-based composites against antibiotic-resistant bacteria: current trends and future perspectives
- PMID: 36968045
- PMCID: PMC10038123
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra01276j
MXene-based composites against antibiotic-resistant bacteria: current trends and future perspectives
Abstract
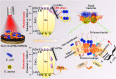
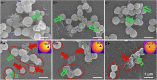
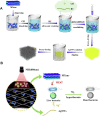
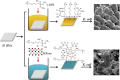
Today, finding novel nanomaterial-based strategies to combat bacterial resistance is an important field of science. MXene-based composites have shown excellent antimicrobial potential owing to their fascinating properties such as excellent photothermal effects, highly active sites, large interlayer spacing, unique chemical structures, and hydrophilicity; they have great potential to damage the bacterial cells by rupturing the bacterial cell membranes, enhancing the permeability across the membrane, causing DNA damages, reducing the metabolic activity, and generating oxidative stress. After inserting into or attaching on the surface of pathogenic bacteria, these two-dimensional structures can cause bacterial membrane disruption and cell content leakage owing to their sharp edges. Remarkably, MXenes and their composites with excellent photothermal performance have been studied in photothermal antibacterial therapy to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria and suppress chronic wound infections, thus providing new opportunities for multidrug-resistant bacteria-infected wound healing. But, details about the possible interactions between MXene-based nanosystems and bacterial cell membranes are rather scarce. Also, the mechanisms of photothermal antibacterial therapy as well as synergistic tactics including photothermal, photodynamic or chemo-photothermal therapy still need to be uncovered. This review endeavors to delineate critical issues pertaining to the application of MXene-based composites against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, focusing on their photocatalytic inactivation, physical damage, and photothermal antibacterial therapy.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare no competing interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MXene: A wonderful nanomaterial in antibacterial.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 1;12:1338539. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1338539. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38361792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Titanium carbide MXene-based hybrid hydrogel for chemo-photothermal combinational treatment of localized bacterial infection.Acta Biomater. 2022 Apr 1;142:113-123. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.02.019. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35189382
-
MXenes Antibacterial Properties and Applications: A Review and Perspective.Small. 2023 Apr;19(14):e2206716. doi: 10.1002/smll.202206716. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Small. 2023. PMID: 36604987 Review.
-
Ti3C2Tx MXene loaded with indocyanine green for synergistic photothermal and photodynamic therapy for drug-resistant bacterium.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022 Sep;217:112663. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112663. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022. PMID: 35785716
-
Multifunctional MXene-doped photothermal microneedles for drug-resistant bacteria-infected wound healing.Biomater Sci. 2024 Jan 30;12(3):660-673. doi: 10.1039/d3bm01676e. Biomater Sci. 2024. PMID: 38063374
Cited by
-
Staphylococcal Drug Resistance: Mechanisms, Therapies, and Nanoparticle Interventions.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Feb 19;18:1007-1033. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S510024. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 39990781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NH2-MXene/OXG nanocomposite hydrogel with efficient photothermal antibacterial activity for potentially removing biofilms.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 19;10(15):e34889. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34889. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157356 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental implications of metal-organic frameworks and MXenes in biomedical applications: a perspective.RSC Adv. 2023 Nov 24;13(49):34562-34575. doi: 10.1039/d3ra07092a. eCollection 2023 Nov 22. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38024989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MXene-based composites in smart wound healing and dressings.Nanoscale Adv. 2024 May 21;6(14):3513-3532. doi: 10.1039/d4na00239c. eCollection 2024 Jul 9. Nanoscale Adv. 2024. PMID: 38989508 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hu T. Mei X. Wang Y. Weng X. Liang R. Wei M. Sci. Bull. 2019;64:1707–1727. - PubMed
-
- Huang K. Li Z. Lin J. Han G. Huang P. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018;47:5109–5124. - PubMed
-
- Hwang S. K. Kang S.-M. Rethinasabapathy M. Roh C. Huh Y. S. Chem. Eng. J. 2020;397:125428.
-
- Murugan C. Sharma V. Murugan R. K. Malaimegu G. Sundaramurthy A. J. Controlled Release. 2019;299:1–20. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

