Risk assessment validation in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: Data from a Southern Brazil registry (RESPHIRAR study)
- PMID: 36968814
- PMCID: PMC10031811
- DOI: 10.1002/pul2.12193
Risk assessment validation in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: Data from a Southern Brazil registry (RESPHIRAR study)
Abstract
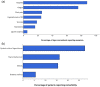
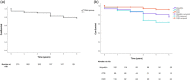
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a severe and progressive disease characterized by increased pulmonary vascular resistance, ultimately leading to right heart failure and death. Registries are a valuable tool in the research of rare conditions such as PAH. Moreover, the risk assessment strategy has been validated in European and North American registries and has been reported to provide an accurate prediction of mortality and the clinical advantage of reaching low-risk status. However, there is no available data from Brazil. Thus, the aim of the present study was to describe the characteristics of a sample of PAH from Southern Brazil and to retrospectively validate the risk assessment at our population. The RESPHIRAR is a retrospective and multicentric registry on pulmonary hypertension. With a join collaboration from nine centers in Southern Brazil, demographics, clinical presentation, and hemodynamics data of PAH were collected between 2007 and 2017. Moreover, the REVEAL 2.0 and REVEAL 2.0 Lite risk assessments were validated in our population. Overall, 370 PAH patients were included in the present study. Patients were predominantly female (78.5%) and had a mean age of 41.8 ± 18.8 years. Most patients (33.4%) had idiopathic PAH, 30.2% had PAH associated with congenital heart disease, and 23.5% had PAH associated with connective tissue disease. The low-risk group showed significantly lower mortality than the intermediated- or high-risk group at diagnosis (p < 0.05). In conclusion, our data suggest that REVEAL 2.0 and REVEAL 2.0 Lite risk assessments can predict mortality risk in PAH patients in Southern Brazil.
Keywords: Southern Brazil registry; pulmonary arterial hypertension; risk assessment.
© 2023 The Authors. Pulmonary Circulation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
Gláucia Maria Barbieri reports speaker and sponsorships in scientific events by Janssen and Bayer. Ariovaldo Leal Fagundes reports lectures to GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and AstraZeneca. Scientific consultancy fee from Ache, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Chiesi. Roger Pirath Rodrigues reports lectures to Janssen, Bayer, Astra‐Zeneca, GSK. Rogerio Souza reports lecture and consultancy fees from Acceleron, Bayer, and Merck. Gisela Martina Bohns Meyer reports lecture and consultancy fees from Aceeleron, Bayer, and GSK. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest. Conflict of interest outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- McGoon MD, Benza RL, Escribano‐Subias P, Jiang X, Miller DP, Peacock AJ, Pepke‐Zaba J, Pulido T, Rich S, Rosenkranz S, Suissa S, Humbert M. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. JACC. 2013;62(25 suppl):D51–9. - PubMed
-
- Farber HW, Miller DP, Poms AD, Badesch DB, Frost AE, Rouzic EML, Romero AJ, Benton WW, Elliott CG, McGoon MD, Benza RL. Five‐year outcomes of patients enrolled in the REVEAL registry. Chest. 2015;148(4):1043–54. - PubMed
-
- Humbert M. Lessons from pulmonary hypertension registries. Rev Port Cardiol. 2018;37(9):759–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

