Discovery of therapeutic targets of quercetin for endometrial carcinoma patients infected with COVID-19 through network pharmacology
- PMID: 36969077
- PMCID: PMC10031047
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1151434
Discovery of therapeutic targets of quercetin for endometrial carcinoma patients infected with COVID-19 through network pharmacology
Abstract
Purpose: Aimed to identify the anti-uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (UCEC) function and characterize the mechanism of quercetin in the treatment of patients infected with COVID-19 via integrated in silico analysis.
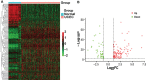
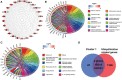
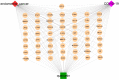
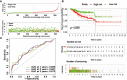
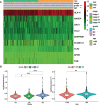
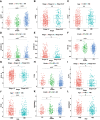
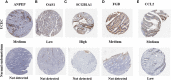
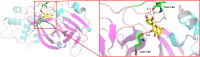
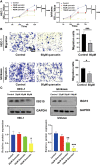
Methods: The Cancer Genome Atlas and Genotype Tissue Expression databases were applied to obtain differentially expressed genes of UCEC and non-tumor tissue. Several in silico methods such as network pharmacology, functional enrichment analysis, Cox regression analyses, somatic mutation analysis, immune infiltration and molecular docking were used to investigate and analysis the biological targets, functions and mechanisms of anti-UCEC/COVID-19 of quercetin. Multiple methods such as CCK8 assay, Transwell assay and western blotting were performed to test proliferation, migration, and protein level of UCEC (HEC-1 and Ishikawa) cells.
Results: Functional analysis disclosed that quercetin against UCEC/COVID-19 mainly by 'biological regulation', 'response to stimulus', and 'regulation of cellular process'. Then, regression analyses indicated that 9 prognostic genes (including ANPEP, OAS1, SCGB1A1, HLA-A, NPPB, FGB, CCL2, TLR4, and SERPINE1) might play important roles in quercetin for treating UCEC/COVID-19. Molecular docking analysis revealed that the protein products of 9 prognostic genes were the important anti-UCEC/COVID-19 biological targets of quercetin. Meanwhile, the proliferation and migration of UCEC cells were inhibited by quercetin. Moreover, after treatment with quercetin, the protein level of ubiquitination-related gene ISG15 was decreased in UCEC cells in vitro.
Conclusions: Taken together, this study provides new treatment option for UCEC patients infected with COVID-19. Quercetin may work by reducing the expression of ISG15 and participating in ubiquitination-related pathways.
Keywords: COVID-19; network pharmacology (NP); quercetin; ubiquitination; uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (UCEC).
Copyright © 2023 Li, Liu, Lin, Gu, Xiang and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Self WH, Sandkovsky U, Reilly CS, Vock DM, Gottlieb RL, Mack M, et al. Efficacy and safety of two neutralising monoclonal antibody therapies, sotrovimab and brii-196 plus brii-198, for adults hospitalised with covid-19 (Tico): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis (2022) 22(5):622–35. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(21)00751-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

