Therapeutic Role of ELOVL in Neurological Diseases
- PMID: 36969404
- PMCID: PMC10034982
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00056
Therapeutic Role of ELOVL in Neurological Diseases
Abstract
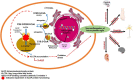
Fatty acids play an important role in controlling the energy balance of mammals. De novo lipogenesis also generates a significant amount of lipids that are endogenously produced in addition to their ingestion. Fatty acid elongation beyond 16 carbons (palmitic acid), which can lead to the production of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA), can be caused by the rate-limiting condensation process. Seven elongases, ELOVL1-7, have been identified in mammals and each has a unique substrate specificity. Researchers have recently developed a keen interest in the elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein 1 (ELOVL1) enzyme as a potential treatment for a variety of diseases. A number of neurological disorders directly or indirectly related to ELOVL1 involve the elongation of monounsaturated (C20:1 and C22:1) and saturated (C18:0-C26:0) acyl-CoAs. VLCFAs and ELOVL1 have a direct impact on the neurological disease. Other neurological symptoms such as ichthyotic keratoderma, spasticity, and hypomyelination have also been linked to the major enzyme (ELOVL1). Recently, ELOVL1 has also been heavily used to treat a number of diseases. The current review focuses on in-depth unique insights regarding the role of ELOVL1 as a therapeutic target and associated neurological disorders.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nie L.; Pascoa T. C.; Pike A. C.; Bushell S. R.; Quigley A.; Ruda G. F.; Chu A.; Cole V.; Speedman D.; Moreira T.; et al. The structural basis of fatty acid elongation by the ELOVL elongases. Nature structural & molecular biology 2021, 28 (6), 512–520. 10.1038/s41594-021-00605-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jung U. J.; Choi M.-S. Obesity and its metabolic complications: the role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. International journal of molecular sciences 2014, 15 (4), 6184–6223. 10.3390/ijms15046184. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials