Role of dynamic ultrasound in assessment of the snapping elbow and distal biceps tendon injury
- PMID: 36969535
- PMCID: PMC10034657
- DOI: 10.1177/1742271X211057204
Role of dynamic ultrasound in assessment of the snapping elbow and distal biceps tendon injury
Abstract
Introduction: Ultrasound is useful in assessing patients with snapping syndromes around the elbow joint. The dynamic nature of the examination allows for direct visualisation of the underlying causative factor.Topic description: We discuss the role of dynamic ultrasound in assessing various snapping syndromes around the elbow, such as ulnar nerve instability, snapping triceps and less commonly, snapping brachialis. Ultrasound is also useful in evaluating the distal biceps tendon, particularly in differentiating partial from complete tendon injury.
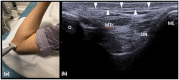
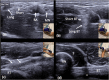
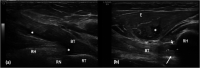
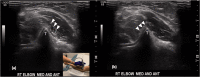
Discussion: Ulnar nerve instability and snapping triceps can be assessed via a medial approach with the transducer placed transversely between the medial epicondyle and the olecranon. In ulnar nerve instability, the nerve can be seen crossing over the medial epicondyle on elbow flexion. In snapping triceps syndrome, both the ulnar nerve and the distal triceps can be seen dislocating over the medial epicondyle. Dynamic assessment of the distal biceps tendon using a lateral approach minimises anisotropy artefact often seen on the anterior approach. Passive pronation and supination of the forearm will reveal little or no movement in a completely torn tendon whereas moving tendon fibres will be appreciated in partial tears. In a snapping brachialis, the medial portion of brachialis will be seen abnormally translocating anterolateral to the medial border of the trochlea during elbow flexion and snapping back into its normal position on elbow extension.
Conclusion: Dynamic ultrasound of the elbow is valuable in diagnosing patients with snapping sensations around the joint and in evaluating the integrity of the distal biceps tendon.
Keywords: Musculoskeletal; brachialis; real-time imaging; tendinopathy; triceps; ulnar nerve.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Mazurek MT, Shin AY. Upper extremity peripheral nerve anatomy: current concepts and applications. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001; 383:7–20. - PubMed
-
- Ozturk E, Sonmez G, Colak A, et al.. Sonographic appearances of the normal ulnar nerve in the cubital tunnel. J Clin Ultrasound 2008; 36:325–329. - PubMed
-
- Yalcin E, Onder B, Akyuz M. Ulnar nerve measurements in healthy individuals to obtain reference values. Rheumatol Int 2013; 33:1143–1147. - PubMed
-
- Kim B-J, Date ES, Lee S-H, et al. Distance measure error induced by displacement of the ulnar nerve when the elbow is flexed. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2005; 86:809–812. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
