Diabetic foot ulcer: A comprehensive review of pathophysiology and management modalities
- PMID: 36970004
- PMCID: PMC10037283
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i8.1684
Diabetic foot ulcer: A comprehensive review of pathophysiology and management modalities
Abstract
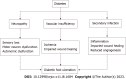
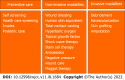
Diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is a debilitating and severe manifestation of uncontrolled and prolonged diabetes that presents as ulceration, usually located on the plantar aspect of the foot. Approximately 15% of individuals with diabetes will eventually develop DFU, and 14%-24% of them will require amputation of the ulcerated foot due to bone infection or other ulcer-related complications. The pathologic mechanisms underlying DFU are comprise a triad: Neuropathy, vascular insufficiency, and secondary infection due to trauma of the foot. Standard local and invasive care along with novel approaches like stem cell therapy pave the way to reduce morbidity, decrease amputations, and prevent mortality from DFU. In this manuscript, we review the current literature with focus on the pathophysiology, preventive options, and definitive management of DFU.
Keywords: Antibiotics; Cell therapy; Diabetes; Foot; Revascularization; Ulcer.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020. [cited 22 October, 2022]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html .
-
- University of California San Francisco. Vascular & Endovascular Surgery - Diabetic Foot Ulcers. [cited 22 October, 2022]. Available from: https://vascularsurgery.ucsf.edu/conditions--procedures/diabetic-foot-ul... .
-
- Boulton AJ, Kirsner RS, Vileikyte L. Clinical practice. Neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:48–55. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources