Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis Linked to COVID-19 Infection: a Case Report
- PMID: 36970581
- PMCID: PMC10031685
- DOI: 10.1007/s42399-023-01450-y
Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis Linked to COVID-19 Infection: a Case Report
Abstract
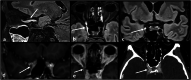
The severity of SARS-CoV-2 virus infection is mainly related to its respiratory complications. However, it can also lead to a large variety of thromboembolic events. Symptoms may include headache, fever, and neurological disorders. Since 2020, the clinical presentation of COVID-19 infection has become increasingly varied, leading in some cases to complex symptom associations, including numerous neurological symptoms. SARS-CoV-2 may lead to neurotropism which could reach the central nervous system and all cranial nerves. Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a rare condition and may occur as a complication of ear, nose, and throat (ENT) or facial infections. A 73-year-old man without personal or family history of thrombosis was referred to the emergency room for a sudden appearance of diplopia and ptosis, 3 days after testing positive for COVID-19 infection. An initial head CT-scan found no signs of stroke. He underwent a cerebral MRI 7 days later, which revealed a thrombosis of his right cavernous sinus. A brain CT scan 7 days later showed regression of the thrombosis with complete recanalization of the cavernous sinus. This was accompanied by a complete regression of diplopia and fever. He was discharged from the hospital 10 days after hospital admission. In this case report, we describe a rare event of cavernous thrombophlebitis following a COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19 infection; Cavernous sinus thrombosis; Neurological symptoms.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kremer S, Lersy F, Anheim M, Merdji H, Schenck M, Oesterlé H, et al. 2020 Neurologic and neuroimaging findings in patients with COVID-19: a retrospective multicenter study. Neurology 29 95(13):186882 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
