Gastrointestinal microbiome and cholelithiasis: Current status and perspectives
- PMID: 36970590
- PMCID: PMC10037248
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i10.1589
Gastrointestinal microbiome and cholelithiasis: Current status and perspectives
Abstract
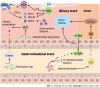
Cholelithiasis is a common digestive disease affecting 10% to 15% of adults. It imposes significant global health and financial burdens. However, the pathogenesis of cholelithiasis involves several factors and is incompletely elucidated. In addition to genetic predisposition and hepatic hypersecretion, the pathogenesis of cholelithiasis might involve the gastrointestinal (GI) microbiome, consisting of microorganisms and their metabolites. High-throughput sequencing studies have elucidated the role of bile, gallstones, and the fecal microbiome in cholelithiasis, associating microbiota dysbiosis with gallstone formation. The GI microbiome may drive cholelithogenesis by regulating bile acid metabolism and related signaling pathways. This review examines the literature implicating the GI microbiome in cholelithiasis, specifically gallbladder stones, choledocholithiasis, and asymptomatic gallstones. We also discuss alterations of the GI microbiome and its influence on cholelithogenesis.
Keywords: Bile acid; Bile microbiome; Cholesterol gallstone; Common bile duct stone; Gallstone; Gastrointestinal microbiome.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Su Z, Gong Y, Liang Z. Prevalence of gallstone in Mainland China: A meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2020;44:e69–e71. - PubMed
-
- Shabanzadeh DM. Incidence of gallstone disease and complications. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2018;34:81–89. - PubMed
-
- Everhart JE, Ruhl CE. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States part I: overall and upper gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:376–386. - PubMed
-
- Shaffer EA. Gallstone disease: Epidemiology of gallbladder stone disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;20:981–996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

