Analytical performance evaluation of Lumipulse® SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay in 392 asymptomatic patients
- PMID: 36972465
- PMCID: PMC10156099
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24867
Analytical performance evaluation of Lumipulse® SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay in 392 asymptomatic patients
Abstract
Introduction: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is one of the current public health care challenges. The main strategy adopted to prevent the spread of infection is the rapid identification of COVID-19-positive subjects. The aim of this study was to compare the performance of Lumipulse® antigen immunoassay with the real-time RT-PCR, the gold standard for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, in a strictly selected asymptomatic population.
Materials and methods: A total of 392 consecutive oro-nasopharyngeal swabs were collected from patients with no symptoms related to COVID-19 at the Emergency Department of AORN Sant'Anna e San Sebastiano, Caserta, Italy to evaluate the analytical performance of Lumipulse® SARS-CoV-2 antigen compared to qualitative real-time RT-PCR in asymptomatic patients.
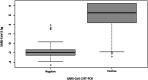
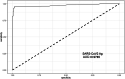
Results: Lumipulse® SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay shows an overall agreement rate of 97% with a sensitivity of 96% and a specificity of 98%, with a PPV and NPV of 97%. The sensitivity varies according to the cycle threshold (Ct )-value reaching 100% and 86% with 15 < Ct < 25 and Ct ≥ 25, respectively. The ROC analysis yielded an AUC value of 0.98, suggesting that the antigen test may accurately detect SARS-CoV-2.
Conclusion: Our data showed that Lumipulse® SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay might be an efficient tool in the identification and limitation of SARS-CoV-2 transmission in large asymptomatic populations.
Keywords: COVID-19; RT-PCR; SARS-CoV-2 antigen; asymptomatic; comparison.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) Weekly epidemiological update and weekly operational update. Accessed August 12, 2022. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel‐coronavirus‐2019/situatio...
-
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center . Accessed August 12, 2022. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus (COVID‐19) Dashboard. Accessed August 12, 2022. https://covid19.who.int/region/euro/country/it
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

