CRISPR-assisted test for Schistosoma haematobium
- PMID: 36973334
- PMCID: PMC10042105
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-31238-y
CRISPR-assisted test for Schistosoma haematobium
Abstract
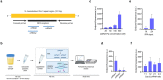
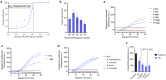
Schistosomiasis is a major neglected tropical disease targeted for elimination as a public health issue by 2030, however there is an urgent need for more sensitive and specific diagnostic tests suitable to resource-limited settings. Here we developed CATSH, a CRISPR-assisted diagnostic test for Schistosoma haematobium, utilising recombinase polymerase amplification, Cas12a-targeted cleavage and portable real-time fluorescence detection. CATSH showed high analytical sensitivity, consistent detection of a single parasitic egg and specificity for urogenital Schistosoma species. Thanks to a novel CRISPR-compatible sample preparation developed using simulated urine samples containing parasitic eggs, CATSH had a sample-to-result within 2 h. The components of CATSH can be lyophilised, reducing cold chain dependence and widening access to lower and middle-income countries. This work presents a new application of CRISPR diagnostics for highly sensitive and specific detection of parasitic pathogens in remote areas and could have a significant impact on the elimination of neglected tropical diseases.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Schistosomiasis. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schistosomiasis.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites - Schistosomiasis. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/schistosomiasis/biology.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

