Exploiting machine learning models to identify novel Alzheimer's disease biomarkers and potential targets
- PMID: 36973386
- PMCID: PMC10043000
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-30904-5
Exploiting machine learning models to identify novel Alzheimer's disease biomarkers and potential targets
Abstract
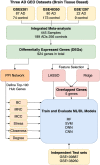
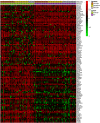
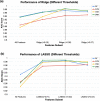
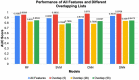
We still do not have an effective treatment for Alzheimer's disease (AD) despite it being the most common cause of dementia and impaired cognitive function. Thus, research endeavors are directed toward identifying AD biomarkers and targets. In this regard, we designed a computational method that exploits multiple hub gene ranking methods and feature selection methods with machine learning and deep learning to identify biomarkers and targets. First, we used three AD gene expression datasets to identify 1/ hub genes based on six ranking algorithms (Degree, Maximum Neighborhood Component (MNC), Maximal Clique Centrality (MCC), Betweenness Centrality (BC), Closeness Centrality, and Stress Centrality), 2/ gene subsets based on two feature selection methods (LASSO and Ridge). Then, we developed machine learning and deep learning models to determine the gene subset that best distinguishes AD samples from the healthy controls. This work shows that feature selection methods achieve better prediction performances than the hub gene sets. Beyond this, the five genes identified by both feature selection methods (LASSO and Ridge algorithms) achieved an AUC = 0.979. We further show that 70% of the upregulated hub genes (among the 28 overlapping hub genes) are AD targets based on a literature review and six miRNA (hsa-mir-16-5p, hsa-mir-34a-5p, hsa-mir-1-3p, hsa-mir-26a-5p, hsa-mir-93-5p, hsa-mir-155-5p) and one transcription factor, JUN, are associated with the upregulated hub genes. Furthermore, since 2020, four of the six microRNA were also shown to be potential AD targets. To our knowledge, this is the first work showing that such a small number of genes can distinguish AD samples from healthy controls with high accuracy and that overlapping upregulated hub genes can narrow the search space for potential novel targets.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

