RU-Net: skull stripping in rat brain MR images after ischemic stroke with rat U-Net
- PMID: 36973775
- PMCID: PMC10045128
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-023-00994-8
RU-Net: skull stripping in rat brain MR images after ischemic stroke with rat U-Net
Abstract
Background: Experimental ischemic stroke models play a fundamental role in interpreting the mechanism of cerebral ischemia and appraising the development of pathological extent. An accurate and automatic skull stripping tool for rat brain image volumes with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are crucial in experimental stroke analysis. Due to the deficiency of reliable rat brain segmentation methods and motivated by the demand for preclinical studies, this paper develops a new skull stripping algorithm to extract the rat brain region in MR images after stroke, which is named Rat U-Net (RU-Net).
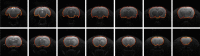
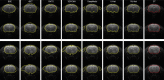
Methods: Based on a U-shape like deep learning architecture, the proposed framework integrates batch normalization with the residual network to achieve efficient end-to-end segmentation. A pooling index transmission mechanism between the encoder and decoder is exploited to reinforce the spatial correlation. Two different modalities of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and T2-weighted MRI (T2WI) corresponding to two in-house datasets with each consisting of 55 subjects were employed to evaluate the performance of the proposed RU-Net.
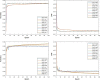
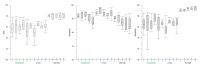
Results: Extensive experiments indicated great segmentation accuracy across diversified rat brain MR images. It was suggested that our rat skull stripping network outperformed several state-of-the-art methods and achieved the highest average Dice scores of 98.04% (p < 0.001) and 97.67% (p < 0.001) in the DWI and T2WI image datasets, respectively.
Conclusion: The proposed RU-Net is believed to be potential for advancing preclinical stroke investigation and providing an efficient tool for pathological rat brain image extraction, where accurate segmentation of the rat brain region is fundamental.
Keywords: Brain segmentation; Deep learning; Ischemic stroke; MRI; Skull stripping; U-Net.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Automatic brain extraction and hemisphere segmentation in rat brain MR images after stroke using deformable models.Med Phys. 2021 Oct;48(10):6036-6050. doi: 10.1002/mp.15157. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34388268
-
Automated joint skull-stripping and segmentation with Multi-Task U-Net in large mouse brain MRI databases.Neuroimage. 2021 Apr 1;229:117734. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.117734. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33454412
-
Automated Stroke Lesion Segmentation in Rat Brain MR Images Using an Encoder-Decoder Framework.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2023 Jul;2023:1-4. doi: 10.1109/EMBC40787.2023.10340278. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2023. PMID: 38083277
-
An open, multi-vendor, multi-field-strength brain MR dataset and analysis of publicly available skull stripping methods agreement.Neuroimage. 2018 Apr 15;170:482-494. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.08.021. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28807870 Review.
-
Methods on Skull Stripping of MRI Head Scan Images-a Review.J Digit Imaging. 2016 Jun;29(3):365-79. doi: 10.1007/s10278-015-9847-8. J Digit Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26628083 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep learning segmentation model for quantification of infarct size in pigs with myocardial ischemia/reperfusion.Basic Res Cardiol. 2024 Dec;119(6):923-936. doi: 10.1007/s00395-024-01081-x. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Basic Res Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39348000 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based automated lesion segmentation on mouse stroke magnetic resonance images.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 16;13(1):13341. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39826-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37587160 Free PMC article.
-
Flood change detection model based on an improved U-net network and multi-head attention mechanism.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 26;15(1):3295. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87851-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39865097 Free PMC article.
-
Fully automated whole brain segmentation from rat MRI scans with a convolutional neural network.J Neurosci Methods. 2024 May;405:110078. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2024.110078. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Neurosci Methods. 2024. PMID: 38340902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- et al: Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141(9):e139-e596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

