Obese asthma phenotypes display distinct plasma biomarker profiles
- PMID: 36973952
- PMCID: PMC10032201
- DOI: 10.1002/clt2.12238
Obese asthma phenotypes display distinct plasma biomarker profiles
Abstract
Background: Obese asthma is a complex phenotype and further characterization of the pathophysiology is needed. This study aimed to explore inflammation-related plasma biomarkers in lean and overweight/obese asthmatics.
Methods: We elucidated levels of inflammation-related plasma proteins in obese asthma phenotypes in the population-based cohort BAMSE (Swedish: Children, Allergy, Milieu, Stockholm, Epidemiology) using data from 2069 24-26-year-olds. Subjects were divided into lean asthma (n = 166), lean controls (n = 1440), overweight/obese asthma (n = 73) and overweight/obese controls (n = 390). Protein levels (n = 92) were analysed using the Olink Proseek Multiplex Inflammation panel.
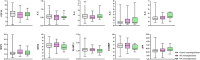
Results: Of the 92 included proteins, 41 were associated with lean and/or overweight/obese asthma. The majority of proteins associated with overweight/obese asthma also associated with overweight/obesity among non-asthmatics. Beta-nerve growth factor (BetaNGF), interleukin 10 (IL-10), and matrix metalloproteinase 10 (MMP10) were associated only with lean asthma while C-C motif chemokine 20 (CCL20), fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19), interleukin 5 (IL-5), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) were associated only with overweight/obese asthma. Overweight/obesity modified the association between asthma and 3 of the proteins: fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), interleukin 4 (IL-4), and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). In the overweight/obese group, interleukin-6 (IL-6) was associated with non-allergic asthma but not allergic asthma.
Conclusion: These data indicate distinct plasma protein phenotypes in lean and overweight/obese asthmatics which, in turn, can impact upon therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: asthma; body mass index; inflammation; obesity; plasma biomarker.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Allergy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
EM reports lecture, consulting or advisory boards fees from AstraZeneca, Chiesi, Novartis and Sanofi outside the submitted work. SK reports lecture or advisory boards fees from Novartis and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. MvH has received lecture fee from Thermo Fisher Scientific outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
- Region Stockholm, ALF project, Clinical postdoctoral appointment (SK), and database maintenance
- Hjärt-Lungfonden
- European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Medium-Term Research Fellowship (NHP)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, reagents for the allergen-specific IgE analyses
- Insamlingsstiftelsen Cancer- och Allergifonden
- 757919/H2020 European Research Council
- LTRF202101-00861/European Respiratory Society (NHP)
- 2016-01646/Svenska Forskningsrådet Formas
- 2017-00526/Forskningsrådet om Hälsa, Arbetsliv och Välfärd
- 2016-03086/Vetenskapsrådet
- 2018-02524/Vetenskapsrådet
- 2019-01060/Vetenskapsrådet
- 2020-02170/Vetenskapsrådet
- Astma- och Allergiförbundet
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

