Evaluation of vertebral shortening and interbody fusion with short segment pedicle screw fixation for unstable thoracolumbar fractures
- PMID: 36974098
- PMCID: PMC10039110
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2023.01.010
Evaluation of vertebral shortening and interbody fusion with short segment pedicle screw fixation for unstable thoracolumbar fractures
Abstract
Background: Various operative procedures have been described for the treatment of traumatic paraplegia caused by unstable thoracolumbar fractures. We prospectively evaluated interbody fusion (IBF) with SS-PSF in these cases with regard to clinico-radiological outcome with the objectives: (1) Does IBF and short segment pedicle screw fixation (SS-PSF) prevent progression of kyphotic angle after surgery? (2) Can this procedure be safely performed in the setting of acute trauma?.
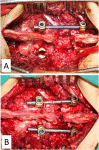
Methods: Sixteen patients suffering from traumatic paraplegia caused by acute unstable thoracolumbar fractures were enrolled prospectively and underwent IBF with SS-PSF. They were evaluated for magnitude of shortening in spine, progression of kyphotic angle, and neurological improvement by American spinal injury association scale (ASIA).
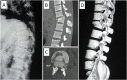
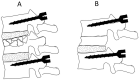
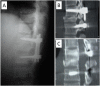
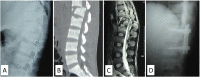
Results: Out of total sixteen, 14 patients were ASIA grade A and 2 were grade C, at the time of presentation. Thirteen out of these 14 remained grade A and one improved to B. Both the patients who had grade C involvement at the time of presentation improved to grade D at one-year follow-up. The mean blood loss was 750 ml (range; 650 ml-1150 ml). Mean kyphotic angle decreased from 20.6° (range; 13° to 37°) preoperatively to 6.2° (range; 3° to 10°) at postoperative day 2 (p = 0.002). Its mean value after 6 months was 6.5° (range; 3° to 11°). The procedure resulted in mean spinal column shortening of 18 mm (range; 16 mm-22 mm) in the spinal column. All the patients achieved bony union by a mean duration of 3.9 months (range; 3 months-6 months).
Conclusions: IBF with SS-PSF has the shortest possible instrumented construct for thoracolumbar junction fusion done by posterior approach. The interbody fusion for unstable thoracolumbar junction fractures prevents the progression of kyphotic angle post-operatively.
Level of evidence: Level 4.
© 2023 Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Rosenthal B.D., Boody B.S., Jenkins T.J., Hsu W.K., Patel A.A., Savage J.W. Thoracolumbar burst fractures. Clin Spine Surg. 2018 May;31(4):143–151. - PubMed
-
- Wood K.B., Li W., Lebl D.S., Ploumis A. Management of thoracolumbar spine fractures. Spine J. 2014 Jan;14(1):145–164. - PubMed
-
- Denis F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine. 1983 Nov-Dec;8(8):817–831. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

