Locus coeruleus-noradrenergic modulation of trigeminal pain: Implications for trigeminal neuralgia and psychiatric comorbidities
- PMID: 36974102
- PMCID: PMC10038791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2023.100124
Locus coeruleus-noradrenergic modulation of trigeminal pain: Implications for trigeminal neuralgia and psychiatric comorbidities
Abstract
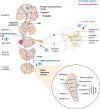
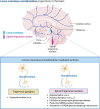
Trigeminal neuralgia is the most common neuropathic pain involving the craniofacial region. Due to the complex pathophysiology, it is therapeutically difficult to manage. Noradrenaline plays an essential role in the modulation of arousal, attention, cognitive function, stress, and pain. The locus coeruleus, the largest source of noradrenaline in the brain, is involved in the sensory and emotional processing of pain. This review summarizes the knowledge about the involvement of noradrenaline in acute and chronic trigeminal pain conditions and how the activity of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons changes in response to acute and chronic pain conditions and how these changes might be involved in pain-related comorbidities including anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbance.
Keywords: Locus coeruleus; Neuropathic pain; Noradrenaline; Trigeminal neuralgia.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Aghajanian G.K., VanderMaelen C.P. alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated hyperpolarization of locus coeruleus neurons: intracellular studies in vivo. Science. 1982;215(4538):1394–1396. - PubMed
-
- Alba-Delgado C., Borges G., Sánchez-Blázquez P., Ortega J.E., Horrillo I., Mico J.A., Meana J.J., Neto F., Berrocoso E. The function of alpha-2-adrenoceptors in the rat locus coeruleus is preserved in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2012;221(1):53–65. - PubMed
-
- Alba-Delgado C., Mico J.A., Sánchez-Blázquez P., Berrocoso E. Analgesic antidepressants promote the responsiveness of locus coeruleus neurons to noxious stimulation: implications for neuropathic pain. Pain. 2012;153(7):1438–1449. - PubMed
-
- Alba-Delgado C., Llorca-Torralba M., Horrillo I., Ortega J.E., Mico J.A., Sánchez-Blázquez P., Meana J.J., Berrocoso E. Chronic pain leads to concomitant noradrenergic impairment and mood disorders. Biol. Psychiatry. 2013;73(1):54–62. - PubMed
-
- Alba-Delgado C., Cebada-Aleu A., Mico J.A., Berrocoso E. Comorbid anxiety-like behavior and locus coeruleus impairment in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A comparative study with the chronic constriction injury model. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2016;71:45–56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

