Characteristics and Occurrence Scenarios of Staff Exposed to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron in Shanghai Lingang Fangcang Shelter Hospital, CHINA
- PMID: 36974103
- PMCID: PMC10039638
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S402282
Characteristics and Occurrence Scenarios of Staff Exposed to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron in Shanghai Lingang Fangcang Shelter Hospital, CHINA
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the characteristics and occurrence scenarios of occupational exposure of staff in the Shanghai Lingang Fangcang Shelter Hospital.
Methods: We collected the data of 80 staff with occupational exposure (including doctors, nurses, cleaning, security guards, and maintenance staff) in the Shanghai Lingang Fangcang Shelter Hospital from April 5 to May 20, 2022. The basic information of occupational exposure, factors influencing different occupational exposure types, ways to discover occupational exposure, discovery places of occupational exposure, and specific occurrence scenarios were compiled and analyzed among these data.
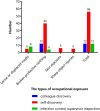
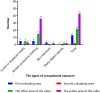
Results: Occupational exposure mainly occurred in nurses (37, 46.25%), and cleaning (21, 26.25%). After the occurrence of occupational exposure, 20 staff (25%) did not know the occurrence time. Moreover, occupational exposure types were listed from high to low proportion as follows: broken protective clothing (56, 70%), mask loosening or displacement (13, 16.25%), skin exposure (6, 7.5%), and sharp object injuries (5, 6.25%). Occupational exposure was discovered mainly through self-discovery (56, 70%), while other discovery ways were majorly colleague discovery (12, 15%) and infection control supervisor discovery (12, 15%). Furthermore, occupational exposure was discovered principally in the public area (53.75%) and the office area (25%) of the cabin, but the proportion of mask loosening or displacement (38.46%) and skin exposure (50%) was also high in the first unloading area. Broken protective clothing occurred in the following scenarios: scratching while working in the cabin (37, 66.07%) and not knowing its occurrence time (25%). The occurrence scenarios of mask loosening or displacement were mainly not knowing its occurrence time (6, 46.15%), self-discovery (3, 23.08%), and at the time of removal (3, 23.08%).
Conclusion: Targeted training and prevention of occupational exposure should be performed to decrease infection risk and ensure staff safety in Fangcang shelter hospitals.
Keywords: Fangcang shelter hospital; SARS-CoV-2 Omicron; characteristics; occupational exposure; scenarios.
© 2023 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Lin JS, Teng XY, Cao Q, Tang J, Ma EX, Chen EZ. Research on the construction and application of information system in large-scale fangcang shelter hospital under COVID-19. J Jinan Univ. 2022;2022:1–7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous