The Impact of COVID-19 on Chinese trade and production: An empirical analysis of processing trade with Japan and the US
- PMID: 36974120
- PMCID: PMC10023200
- DOI: 10.1016/j.asieco.2023.101596
The Impact of COVID-19 on Chinese trade and production: An empirical analysis of processing trade with Japan and the US
Abstract
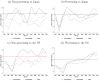
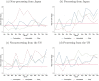
The COVID-19 pandemic severely disrupted international trade, leading countries to grapple with product shortages and firms to experience major supply chain issues. These challenges increased production costs and significantly contributed to lower trade and higher inflation. In this paper, we examine the impact of COVID-19 on Chinese trade through its two main trading partners: Japan and the US. By differentiating products by product type and processing status, we find evidence that products in the middle of the global supply chain were most affected by the pandemic and that the severity of the shock depends on the partner country's role in the global supply chain. Additionally, we find that Chinese exports are more impacted than Chinese imports, regardless of processing status. These findings are largely consistent with economic theory. Understanding that the effects of global shocks vary by product and country will help guide policies that minimize supply chain disruptions.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chinese processing trade; Supply chains.
© 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Barro Robert J, Ursúa José F, Weng Joanna. National Bureau of Economic Research; 2020. The coronavirus and the great influenza pandemic: lessons from the spanish flu for the Coronavirus’s potential effects on mortality and economic activity: Technical report.
-
- Besedeš T., Murshid A.P. Georgia Institute of Technology; 2019. Experimenting with ash: the trade-effects of airspace closures in the aftermath of eyjafjallajökull: Technical report, working paper.
-
- Carvalho Vasco M, Nirei Makoto, Saito Yukiko U, Tahbaz-Salehi Alireza. Supply chain disruptions: Evidence from the great east Japan earthquake. Quarterly Journal of Economics. 2021;136:1255–1321.
-
- Chen Frank, Drezner Zvi, Ryan Jennifer K, Simchi-Levi David. Quantifying the bullwhip effect in a simple supply chain: The impact of forecasting, lead times, and information. Management Science. 2000;46:436–443.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

