Predictive Model of Functional Exercise Compliance of Patients with Breast Cancer Based on Decision Tree
- PMID: 36974132
- PMCID: PMC10039631
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S386405
Predictive Model of Functional Exercise Compliance of Patients with Breast Cancer Based on Decision Tree
Abstract
Objective: Regular functional exercise can help recover the functions of upper limb for patients with breast cancer. By finding the influencing factors of functional exercise compliance and constructing a predictive model, patients with a poor functional exercise compliance can be better identified. This study aims to find out the factors influencing the functional exercise compliance of patients with breast cancer and build a predictive model based on decision tree.
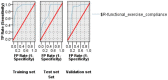
Methods: Convenience sampling was used at two tertiary hospitals in Shantou from August 2020 to March 2021. Data of patients with breast cancer patient was obtained from questionnaires and based on demographics, Constant-Murley Score, Functional Exercise Compliance Scale for Postoperative Breast Cancer Patients, Champion Health Belief Model Scale, Social Support Rating Scale, Disease Perception Questionnaire and Family Care Index Questionnaire. Possible influencing factors of functional exercise compliance were analyzed using correlation analysis as well as univariate and binary logistic regression analysis through SPSS v25, and a CHAID decision tree was used to construct a predictive model on training, validation and test sets via SPSS Modeler v18 at a ratio of 6:2:2. Prediction accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and AUC were used to analyze the efficacy of the predictive model.
Results: A total of 227 valid samples were collected, of which 145 were assessed with a poor compliance (63.9%). According to a logistic regression analysis, perceived benefits, time after surgery and self-efficacy were influencing factors. The prediction accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and AUC of the predictive model, based on a CHAID decision tree analysis, were 70.73%, 57.1%, 77.8% and 0.81 respectively.
Conclusion: The predictive model, based on a CHAID decision tree analysis, had a moderate predictive efficacy, which could be used as a clinical auxiliary tool for clinical nurses to predict patients' functional exercise compliance.
Keywords: breast cancer; decision tree; functional exercise; predictive model.
© 2023 Luo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Yiru Wang has received research funding that is not related to the content of the present manuscript. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou K, Wang W, An J, Li M, Li J, Li X. Effects of progressive upper limb exercises and muscle relaxation training on upper limb function and health-related quality of life following surgery in women with breast cancer: a clinical randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(7):2156–2165. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07305-y - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xin YH, Hu CY, Xiao CR, Liu Y, Sun HP. Application of staged rehabilitation video exercise in functional exercise after breast cancer surgery. Chin J Rehabil Med. 2018;33(4):469–471.
-
- Zhang HT, Li Y, Chen R, Zhang LJ, Qin HY. Longitudinal study of limb functional exercise compliance after breast cancer surgery. Chin J Pract Nurs. 2020;36(20):1554–1559.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources