SARS-CoV-2 strain wars continues: Chemical and thermodynamic characterization of live matter and biosynthesis of Omicron BN.1, CH.1.1 and XBC variants
- PMID: 36974134
- PMCID: PMC10032061
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mran.2023.100260
SARS-CoV-2 strain wars continues: Chemical and thermodynamic characterization of live matter and biosynthesis of Omicron BN.1, CH.1.1 and XBC variants
Abstract
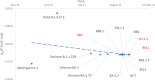
SARS-CoV-2 has during the last 3 years mutated several dozen times. Most mutations in the newly formed variants have been chemically and thermodynamically characterized. New variants have been declared as variants under monitoring. The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control has suggested the hypothesis that the new BN.1, CH.1.1 and XBC variants could have properties similar to those of VOC. Thermodynamic properties of new variants have been reported in this manuscript for the first time. Gibbs energy of biosynthesis, as the driving force for viral multiplication, is less negative for the new variants than for the earlier variants. This indicates that the virus has evolved towards decrease in pathogenicity, which leads to less severe forms of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Enthalpy; Entropy; Gibbs energy; Permissiveness coefficient; Variant under monitoring.
© 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Annamalai K. Oxygen Deficient (OD) Combustion and Metabolism: Allometric Laws of Organs and Kleiber's Law from OD Metabolism? Systems. 2021;9(3):54. doi: 10.3390/systems9030054. Retrieved from. - DOI
-
- Atkins P.W., de Paula J. 2nd edition. W. H. Freeman and Company; 2011. Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences. ISBN-13: 978-1429231145.
-
- Atkins P.W., de Paula J. 10th Edition. W. H. Freeman and Company; New York: 2014. Physical Chemistry: Thermodynamics, Structure, and Change. ISBN-13: 978-1429290197.
-
- Battley E.H., Stone J.R. A comparison of values for the entropy and the entropy of formation of selected organic substances of biological importance in the solid state, as determined experimentally or calculated empirically. Thermochimica acta. 2000;349(1-2):153–161. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6031(99)00509-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
