Comprehensive evaluation of the effect of five sterilization methods on the quality of black carrot juice based on PCA, TOPSIS and GRA models
- PMID: 36974191
- PMCID: PMC10039260
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100604
Comprehensive evaluation of the effect of five sterilization methods on the quality of black carrot juice based on PCA, TOPSIS and GRA models
Abstract
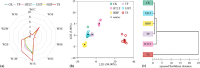
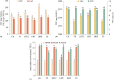
The effect of thermal pasteurization (TP), high temperature long time (HTLT), ultra-high temperature instantaneous (UHT), high hydrostatic pressure (HHP) and thermosonication (TS) sterilization on the physicochemical, sensory and functional properties of black carrot juice (BCJ) were studied. And for the first time, the comprehensive quality of sterilized BCJ was quantified by mathematical modeling. UHT was the least suitable sterilization method for BCJ resulting from the most severe deterioration in functional properties. TS had adverse effects on sensory and physicochemical properties, but significantly increased the total flavonoids and anthocyanins contents (p < 0.05) and showed the strongest antioxidant activity, making it a nutritional high-value processing method. TP and HHP balanced the improvement of sensory properties and the retention of functional properties, which were the most suitable sterilization methods for BCJ. This study determined the optimal sterilization methods of BCJ, and provided a scientific solution for the screening of high quality processing methods.
Keywords: Black carrot juice; Comprehensive evaluation model; High hydrostatic pressure; Thermal sterilization; Thermosonication.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Akhtar S., Rauf A., Imran M., Qamar M., Riaz M., Mubarak M.S. Black carrot (daucus carota L.), dietary and health promoting perspectives of its polyphenols: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2017;66:36–47. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.05.004. - DOI
-
- Anaya-Esparza L.M., Velázquez-Estrada R.M., Roig A.X., García-Galindo H.S., Sayago-Ayerdi S.G., Montalvo-González E. Thermosonication: An alternative processing for fruit and vegetable juices. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2017;61:26–37. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2016.11.020. - DOI
-
- Cejudo-Bastante M.J., Rodríguez-Morgado B., Jara-Palacios M.J., Rivas-Gonzalo J.C., Parrado J., Heredia F.J. Pre-fermentative addition of an enzymatic grape seed hydrolysate in warm climate winemaking. effect on the differential colorimetry, copigmentation and polyphenolic profiles. Food Chemistry. 2016;209:348–357. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.04.092. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Carvalho, Lucia Maria Jaeger, Gomes, P. B., Godoy, Ronoel Luiz de Oliveira, Pacheco, S., do Monte, Pedro Henrique Fernandes, de Carvalho, José Luiz Viana, Nutti, M. R., Neves, A. C. L., Vieira, Ana Carolina Rodrigues Alves, & Ramos, S. R. R. (2012). Total carotenoid content, α-carotene and β-carotene, of landrace pumpkins (cucurbita moschata duch): A preliminary study. Food Research International, 47(2), 337-340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.07.040.
-
- Dereli U., Türkyilmaz M., Yemiş O., Özkan M. Effects of clarification and pasteurization on the phenolics, antioxidant capacity, color density and polymeric color of black carrot (daucus Carota L.) juice. Journal of Food Biochemistry. 2015;39(5):528–537. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12155. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

