Signaling Pathways of the Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins
- PMID: 36974712
- PMCID: PMC10502586
- DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnad008
Signaling Pathways of the Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins
Abstract
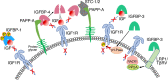
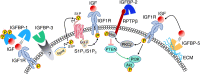
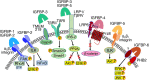
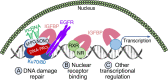
The 6 high-affinity insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) are multifunctional proteins that modulate cell signaling through multiple pathways. Their canonical function at the cellular level is to impede access of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 and IGF-2 to their principal receptor IGF1R, but IGFBPs can also inhibit, or sometimes enhance, IGF1R signaling either through their own post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation or limited proteolysis, or by their interactions with other regulatory proteins. Beyond the regulation of IGF1R activity, IGFBPs have been shown to modulate cell survival, migration, metabolism, and other functions through mechanisms that do not appear to involve the IGF-IGF1R system. This is achieved by interacting directly or functionally with integrins, transforming growth factor β family receptors, and other cell-surface proteins as well as intracellular ligands that are intermediates in a wide range of pathways. Within the nucleus, IGFBPs can regulate the diverse range of functions of class II nuclear hormone receptors and have roles in both cell senescence and DNA damage repair by the nonhomologous end-joining pathway, thus potentially modifying the efficacy of certain cancer therapeutics. They also modulate some immune functions and may have a role in autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. IGFBPs have been proposed as attractive therapeutic targets, but their ubiquity in the circulation and at the cellular level raises many challenges. By understanding the diversity of regulatory pathways with which IGFBPs interact, there may still be therapeutic opportunities based on modulation of IGFBP-dependent signaling.
Keywords: IGF; IGF binding protein; cell-surface; nucleus; receptor; signaling.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins: interactions with IGFs and intrinsic bioactivities.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000 Jun;278(6):E967-76. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.2000.278.6.E967. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000. PMID: 10826997 Review.
-
Quantitative analysis of insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins to identify control mechanisms for insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor phosphorylation.BMC Syst Biol. 2016 Feb 9;10:15. doi: 10.1186/s12918-016-0263-6. BMC Syst Biol. 2016. PMID: 26861122 Free PMC article.
-
What Happened to the IGF Binding Proteins?Endocrinology. 2018 Feb 1;159(2):570-578. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-00908. Endocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29165552 Review.
-
Cellular actions of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins.Horm Metab Res. 1999 Feb-Mar;31(2-3):192-202. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-978719. Horm Metab Res. 1999. PMID: 10226802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF-binding proteins.J Mol Endocrinol. 2018 Jul;61(1):T11-T28. doi: 10.1530/JME-17-0254. Epub 2017 Dec 18. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29255001 Review.
Cited by
-
The multifaceted role of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 16;12:1420862. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1420862. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39081862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Megestrol acetate plus metformin for fertility-sparing treatment of atypical endometrial hyperplasia and early-stage endometrial adenocarcinoma: a prospective study].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Nov 20;44(11):2055-2062. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.01. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39623260 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The signaling landscape of insulin-like growth factor 1.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jan;301(1):108047. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.108047. Epub 2024 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39638246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Side-to-side characterisation of cellular content, soluble factors and in vitro potential on chondrocytes for bone marrow aspirate concentrate and adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction.J Exp Orthop. 2025 May 12;12(2):e70254. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.70254. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Exp Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40357029 Free PMC article.
-
Pantothenic acid ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by targeting IGFBP6 to regulate the TGF-β/SMADs pathway.Commun Biol. 2025 Jul 29;8(1):1127. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08527-5. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40730679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sato A, Nishimura S, Ohkubo T, et al. . Three-dimensional structure of human insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) determined by 1H-NMR and distance geometry. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1993;41(5):433‐440. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1993.tb00462.x - PubMed
-
- Vajdos FF, Ultsch M, Schaffer ML, et al. . Crystal structure of human insulin-like growth factor-1: detergent binding inhibits binding protein interactions. Biochemistry. 2001;40(37):11022‐11029. doi: 10.1021/bi0109111 - PubMed
-
- Baxter RC. The somatomedins: insulin-like growth factors. Adv Clin Chem. 1986;25:49‐115. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60124-9 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

