Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuresis: From Pathophysiology to Management
- PMID: 36974717
- PMCID: PMC10502587
- DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnad010
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuresis: From Pathophysiology to Management
Abstract
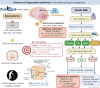
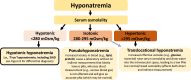
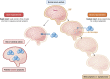
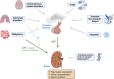
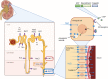
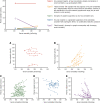
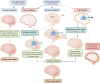
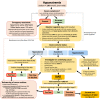
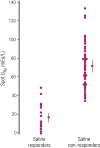
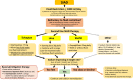
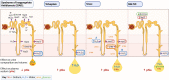
Hyponatremia is the most common electrolyte disorder, affecting more than 15% of patients in the hospital. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIAD) is the most frequent cause of hypotonic hyponatremia, mediated by nonosmotic release of arginine vasopressin (AVP, previously known as antidiuretic hormone), which acts on the renal V2 receptors to promote water retention. There are a variety of underlying causes of SIAD, including malignancy, pulmonary pathology, and central nervous system pathology. In clinical practice, the etiology of hyponatremia is frequently multifactorial and the management approach may need to evolve during treatment of a single episode. It is therefore important to regularly reassess clinical status and biochemistry, while remaining alert to potential underlying etiological factors that may become more apparent during the course of treatment. In the absence of severe symptoms requiring urgent intervention, fluid restriction (FR) is widely endorsed as the first-line treatment for SIAD in current guidelines, but there is considerable controversy regarding second-line therapy in instances where FR is unsuccessful, which occurs in around half of cases. We review the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and differential diagnosis of SIAD, and summarize recent evidence for therapeutic options beyond FR, with a focus on tolvaptan, urea, and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
Keywords: empagliflozin; fluid restriction; hyponatremia; sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i); syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIAD); tolvaptan; urea.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

References
-
- Schwartz WB, Bennett W, Curelop S, Bartter FC. A syndrome of renal sodium loss and hyponatremia probably resulting from inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Med. 1957;23(4):529‐542. - PubMed
-
- Verbalis JG. Whole-body volume regulation and escape from antidiuresis. Am J Med. 2006;119(7 Suppl 1):S21‐S29. - PubMed
-
- Verbalis JG, Goldsmith SR, Greenberg A, et al. Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of hyponatremia: expert panel recommendations. Am J Med. 2013;126(10 Suppl 1):S1‐42. - PubMed
-
- Bartter FC, Schwartz WB. The syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Med. 1967;42(5):790‐806. - PubMed
-
- Vaswani SK, Sprague R. Pseudohyponatremia in multiple myeloma. South Med J. 1993;86(2):251‐252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

