Pentose Pathway Activation Is Superior to Increased Glycolysis for Therapeutic Angiogenesis in Peripheral Arterial Disease
- PMID: 36974760
- PMCID: PMC10122893
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.122.027986
Pentose Pathway Activation Is Superior to Increased Glycolysis for Therapeutic Angiogenesis in Peripheral Arterial Disease
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Pentose Pathway Activation Is Superior to Increased Glycolysis for Therapeutic Angiogenesis in Peripheral Arterial Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Jun 6;12(11):e027703. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.027703. Epub 2023 Jun 1. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37260028 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
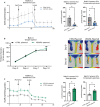
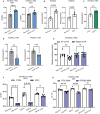
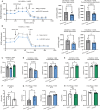
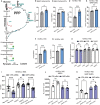
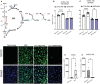
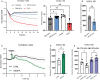
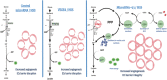
Background In endothelial cells (ECs), glycolysis, regulated by PFKFB3 (6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase, isoform-3), is the major metabolic pathway for ATP generation. In preclinical peripheral artery disease models, VEGF165a (vascular endothelial growth factor165a) and microRNA-93 both promote angiogenesis. Methods and Results Mice following hind-limb ischemia (HLI) and ECs with, and without, hypoxia and serum starvation were examined with, and without, microRNA-93 and VEGF165a. Post-HLI perfusion recovery was monitored. EC metabolism was studied using seahorse assay, and the expression and activity of major metabolism genes were assessed. Reactive oxygen species levels and EC permeability were evaluated. C57Bl/6J mice generated a robust angiogenic response to HLI, with ECs from ischemic versus nonischemic muscle demonstrating no increase in glycolysis. Balb/CJ mice generated a poor angiogenic response post-HLI; ischemic versus nonischemic ECs demonstrated significant increase in glycolysis. MicroRNA-93-treated Balb/CJ mice post-HLI showed better perfusion recovery, with ischemic versus nonischemic ECs showing no increase in glycolysis. VEGF165a-treated Balb/CJ mice post-HLI showed no improvement in perfusion recovery with ischemic versus nonischemic ECs showing significant increase in glycolysis. ECs under hypoxia and serum starvation upregulated PFKFB3. In ECs under hypoxia and serum starvation, VEGF165a versus control significantly upregulated PFKFB3 and glycolysis, whereas miR-93 versus control demonstrated no increase in PFKFB3 or glycolysis. MicroRNA-93 versus VEGF165a upregulated glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression and activity, activating the pentose phosphate pathway. MicroRNA-93 versus control increased reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate and virtually eliminated the increase in reactive oxygen species. In ECs under hypoxia and serum starvation, VEGF165a significantly increased and miR-93 decreased EC permeability. Conclusions In peripheral artery disease, activation of the pentose phosphate pathway to promote angiogenesis may offer potential therapeutic advantages.
Keywords: VEGFA; endothelial metabolism; glycolysis; hypoxia dependent angiogenesis; microRNA‐93; pentose phosphate pathway; vascular permeability.
Figures
References
-
- Yetkin‐Arik B, Vogels IMC, Nowak‐Sliwinska P, Weiss A, Houtkooper RH, Van Noorden CJF, Klaassen I, Schlingemann RO. The role of glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration in the formation and functioning of endothelial tip cells during angiogenesis. Sci Rep. 2019;9:12608. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48676-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Ke X, Fu W, Gao X, Zhang H, Wang W, Ma N, Zhao M, Hao X, Zhang Z. Inhibition of hypoxia‐induced retinal angiogenesis by specnuezhenide, an effective constituent of Ligustrum lucidum Ait., through suppression of the HIF‐1α/VEGF signaling pathway. Molecules. 2016;21:1756. doi: 10.3390/molecules21121756 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

