Shared Leadership and Improvisation: Dual Perspective of Cognition-Affection
- PMID: 36975290
- PMCID: PMC10045884
- DOI: 10.3390/bs13030265
Shared Leadership and Improvisation: Dual Perspective of Cognition-Affection
Abstract
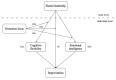
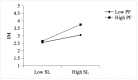
Improvisation is an effective way to cope with rapid changes and obtain unexpected opportunities in a complex environment. Based on the cognitive-affective system theory, this study investigates the dual mediating role of cognitive flexibility and emotional intelligence between shared leadership and improvisation and the moderating role of promotion focus. We used multilevel and multi-sourced data to test the theoretical model and used a social network approach to measure shared leadership in teams. Our sample was comprised of 40 teams and 240 team members. The empirical findings indicated that cognitive flexibility and emotional intelligence mediated the relationship between shared leadership and improvisation; promotion focus moderated the relationship between shared leadership and improvisation, and the mediation effect via cognitive flexibility. This study contributes to expanding on improvisation research from the perspective of shared leadership and incorporating both the cognitive and the emotional process of the generation of improvisation into a theoretical framework from a compound perspective, which will open the black box for the mediation mechanism from shared leadership to improvisation. Furthermore, promotion focus is introduced into the research and creatively corresponds to the cognition-affection mediation mechanism, which expands the applicable scope of the regulatory focus theory.
Keywords: cognitive flexibility; emotional intelligence; improvisation; promotion focus; shared leadership.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hu L., Gu J., Wu J., Lado A.A. Regulatory focus, environmental turbulence, and entrepreneur improvisation. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2018;14:129–148. doi: 10.1007/s11365-017-0446-7. - DOI
-
- Abrantes A.C.M., Cunha M.P., Miner A.S. Elgar Introduction to Organizational Improvisation Theory. Edward Elgar Publishing; Cheltenham, UK: 2022.
-
- Miner A.S., Bassof P., Moorman C. Organizational improvisation and learning: A field study. Adm. Sci. Q. 2001;46:304–337. doi: 10.2307/2667089. - DOI
-
- Nisula A.M. The relationship between supervisor support and individual improvisation. Leadersh. Org. Dev. J. 2015;36:473–488. doi: 10.1108/LODJ-07-2013-0098. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources