Gal-3 Protein Expression and Localization in Prostate Tumours
- PMID: 36975419
- PMCID: PMC10047320
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol30030206
Gal-3 Protein Expression and Localization in Prostate Tumours
Abstract
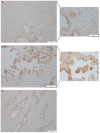
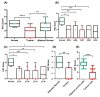
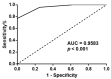
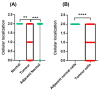
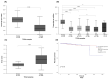
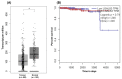
Gal-3 plays an important role in cell survival, mRNA splicing, and cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. Depending on its cellular localization and cancer type, Gal-3 may have tumour-suppressive or tumour-promoting activities. Given the promising diagnostic role of Gal-3 in the urine of PCa patients found in our previous study, its concordant gene and protein expression levels, and its involvement in PCa-related biological processes (e.g., morphogenesis of the prostate gland epithelium), we aimed to investigate this protein immunohistochemically in tumour and normal prostate tissues. Gal-3 protein expression was evaluated in 48 tumour prostate tissues, eight normal prostate tissues and 14 adjacent-normal prostate tissues. Decreased Gal-3 staining was detected in tumour tissues compared with normal tissues. Although Gal-3 staining was decreased in tumour tissues with GS 5-8 and pT2 and pT3 stages compared with normal prostate tissue, no correlation was found between Gal-3 expression and PCa progression. In the present study, the pattern of cellular localization differed between groups, as Gal-3 was predominantly excluded from the nucleus in tumour tissues. Furthermore, Gal-3 had no significant effect on survival and relapse in these PCa patients. This work confirms Gal-3 as a promising marker for PCa diagnosis.
Keywords: Galectin-3; localization; marker; patient survival; prostate cancer; prostate tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gong H.C., Honjo Y., Nangia-Makker P., Hogan V., Mazurak N., Bresalier R., Raz A. The NH2 terminus of galectin-3 governs cellular compartmentalization and functions in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1999;59:6239–6245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

