The Impact of the Blood Lipids Levels on Arterial Stiffness
- PMID: 36975891
- PMCID: PMC10056627
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd10030127
The Impact of the Blood Lipids Levels on Arterial Stiffness
Abstract
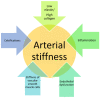
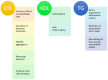
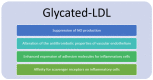
Arterial stiffness is a recognized predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and death. It is an early indicator of arteriosclerosis and is influenced by numerous risk factors and biological processes. The lipid metabolism is crucial and standard blood lipids, non-conventional lipid markers and lipid ratios are associated with arterial stiffness. The objective of this review was to determine which lipid metabolism marker has a greater correlation with vascular aging and arterial stiffness. Triglycerides (TG) are the standard blood lipids that have the strongest associations with arterial stiffness, and are often linked to the early stages of cardiovascular diseases, particularly in patients with low LDL-C levels. Studies often show that lipid ratios perform better overall than any of the individual variables used alone. The relation between arterial stiffness and TG/HDL-C has the strongest evidence. It is the lipid profile of atherogenic dyslipidemia that is found in several chronic cardio-metabolic disorders, and is considered one of the main causes of lipid-dependent residual risk, regardless of LDL-C concentration. Recently, the use of alternative lipid parameters has also been increasing. Both non-HDL and ApoB are very well correlated with arterial stiffness. Remnant cholesterol is also a promising alternative lipid parameter. The findings of this review suggest that the main focus should be on blood lipids and arterial stiffness, especially in individuals with cardio-metabolic disorders and residual cardiovascular risk.
Keywords: arterial stiffness; atherogenic dyslipidemia; blood lipids; residual cardio-vascular risk; vascular aging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Gkaliagkousi E., Lazaridis A., Dogan S., Fraenkel E., Tuna B.G., Mozos I., Vukicevic M., Yalcin O., Gopcevic K. Theories and Molecular Basis of Vascular Aging: A Review of the Literature from VascAgeNet Group on Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Vascular Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:8672. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158672. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vlachopoulos C., Xaplanteris P., Aboyans V., Brodmann M., Cifkova R., Cosentino F., Carlo M.D., Gallino A., Landmesser U., Laurent S., et al. The role of vascular biomarkers for primary and secondary prevention. A position paper from the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on peripheral circulation. Atherosclerosis. 2015;241:507–532. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.05.007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

