Cocoa Consumption Decreases Oxidative Stress, Proinflammatory Mediators and Lipid Peroxidation in Healthy Subjects: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Dose-Response Clinical Trial
- PMID: 36976481
- PMCID: PMC10232545
- DOI: 10.1007/s40292-023-00571-8
Cocoa Consumption Decreases Oxidative Stress, Proinflammatory Mediators and Lipid Peroxidation in Healthy Subjects: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Dose-Response Clinical Trial
Abstract
Introduction: Cocoa flavonoids have been described to reduce the cardiovascular risk. Nevertheless, the involved mechanisms should be clarified and the dose-effect relation has never been evaluated.
Aim: To investigate the dose-dependent effects of cocoa flavonoids on markers of endothelial and platelet activation and oxidative stress.
Methods: According to a randomized, double-blind, controlled, cross-over design, 20 healthy nonsmokers were assigned to receive either five treatments with daily intake of 10 g cocoa (0, 80, 200, 500 and 800 mg cocoa flavonoids/day) in five periods lasting 1 week each.
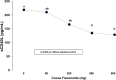
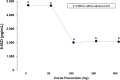
Results: Compared with flavonoid-free cocoa control, cocoa reduced sICAM-1 mean values [from 1190.2 to 1123.0; 906.3; 741.7 and 625.6 pg/mL (p = 0.0198 and p = 0.0016, for 500 and 800 mg respectively], sCD40L mean values [from 218.8 to 210.2; 165.5; 134.5 and 128.4 pg/mL (p = 0.023 and p = 0.013, for 500 and 800 mg respectively] and 8-isoprostanes F2 mean values [from 4703.9 to 4670.7; 2000.1; 2098.4 and 2052.3 pg/mL (p = 0.025; p = 0.034 and p = 0.029, for 200, 500 and 800 mg respectively)].
Conclusions: In our study we observed that short-term cocoa consumption improved proinflammatory mediators, lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress with a significant effect for higher dosages of flavonoids. Our findings suggest cocoa might be a valid tool for dietary intervention in prevention of atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular protection; Cocoa; Endothelial activation; Endothelium; Flavonoids; Oxidative stress.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Davide Grassi, Francesca Mai, Martina De Feo, Remo Barnabei, Augusto Carducci, Giovambattista Desideri, Stefano Necozione, Leen Allegaert, Herwig Bernaert and Claudio Ferri declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest that might be relevant to this work.
Figures

References
-
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1459–544. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

