Validation of web-based audiometry version of HEARZAP
- PMID: 36976819
- PMCID: PMC10047537
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283519
Validation of web-based audiometry version of HEARZAP
Abstract
Aim: The purpose of this study was to verify the accuracy of the web-based audiometer HEARZAP in determining hearing thresholds for both air and bone conduction.
Method: Using a cross-sectional validation design, the web-based audiometer was compared to a gold standard audiometer. Participants in the study totaled 50 (100 ears), of which 25 (50 ears) had normal hearing sensitivity and 25 (50 ears) had various types and degrees of hearing loss. All subjects underwent pure tone audiometry, including air and bone conduction thresholds, using the web-based and gold standard audiometers in a random order. A pause between the two tests was allowed if the patient felt comfortable. The testing for the web-based audiometer and gold standard audiometer was done by two different audiologists with similar qualifications in order to eliminate tester bias. Both the procedures were performed in a sound treated room.
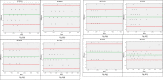
Results: For air conduction thresholds and bone conduction thresholds, respectively, the mean discrepancies between the web-based audiometer and the gold standard audiometer were 1.22 dB HL (SD = 4.61) and 0.8 dB HL (SD = 4.1). The ICC for air conduction thresholds between the two techniques was 0.94 and for the bone conduction thresholds was 0.91. The Bland Altman plots likewise indicated excellent reliability between the two measurements, with the mean difference between the HEARZAP and the gold standard audiometry falling within the top and lower limits of agreement.
Conclusion: The web-based audiometry version of HEARZAP produced precise findings for hearing thresholds that were comparable to those obtained from an established gold standard audiometer. HEARZAP, has the potential to support multi-clinic functionality and enhance service access.
Copyright: © 2023 Pandi Renganath, Ramkumar. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exists
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. World Report On Hearing. Human Rights Watch. 2021. Available: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/world-report-on-hearing
-
- Jayawardena A, Waller B, Edwards B, Larsen-Reindorf R, Esinam Anomah J, Frimpong B, et al.. Portable audiometric screening platforms used in low-resource settings: A review. Journal of Laryngology and Otology. Cambridge University Press; 2019. pp. 74–79. doi: 10.1017/S0022215118001925 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krumm M. a Review of Contemporary Tele-Audiology Literature. J Hear Sci. 2016;6: 9–21. doi: 10.17430/899978 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

