Stimulatory effect of imeglimin on incretin secretion
- PMID: 36977210
- PMCID: PMC10204172
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.14001
Stimulatory effect of imeglimin on incretin secretion
Abstract
Aims/introduction: Imeglimin is a new antidiabetic drug structurally related to metformin. Despite this structural similarity, only imeglimin augments glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS), with the mechanism underlying this effect remaining unclear. Given that glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) also enhance GSIS, we examined whether these incretin hormones might contribute to the pharmacological actions of imeglimin.
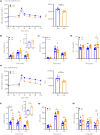
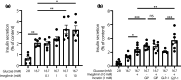
Materials and methods: Blood glucose and plasma insulin, GIP, and GLP-1 concentrations were measured during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) performed in C57BL/6JJcl (C57BL/6) or KK-Ay/TaJcl (KK-Ay) mice after administration of a single dose of imeglimin with or without the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin or the GLP-1 receptor antagonist exendin-9. The effects of imeglimin, with or without GIP or GLP-1, on GSIS were examined in C57BL/6 mouse islets.
Results: Imeglimin lowered blood glucose and increased plasma insulin levels during an OGTT in both C57BL/6 and KK-Ay mice, whereas it also increased the plasma levels of GIP and GLP-1 in KK-Ay mice and the GLP-1 levels in C57BL/6 mice. The combination of imeglimin and sitagliptin increased plasma insulin and GLP-1 levels during the OGTT in KK-Ay mice to a markedly greater extent than did either drug alone. Imeglimin enhanced GSIS in an additive manner with GLP-1, but not with GIP, in mouse islets. Exendin-9 had only a minor inhibitory effect on the glucose-lowering action of imeglimin during the OGTT in KK-Ay mice.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the imeglimin-induced increase in plasma GLP-1 levels likely contributes at least in part to its stimulatory effect on insulin secretion.
Keywords: Glucagon-like peptide-1; Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion; Imeglimin.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Yendapally R, Sikazwe D, Kim SS, et al. A review of phenformin, metformin, and imeglimin. Drug Dev Res 2020; 81: 390–401. - PubMed
-
- Fouqueray P, Leverve X, Fontaine E, et al. Imeglimin – a new oral anti‐diabetic that targets the three key defects of type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Metab 2011; 2: 126.
-
- Pacini G, Mari A, Fouqueray P, et al. Imeglimin increases glucose‐dependent insulin secretion and improves beta‐cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015; 17: 541–545. - PubMed
-
- Vial G, Chauvin MA, Bendridi N, et al. Imeglimin normalizes glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity and improves mitochondrial function in liver of a high‐fat, high‐sucrose diet mice model. Diabetes 2015; 64: 2254–2264. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

