Blunted humoral immune response to the fourth dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in patients undergoing hemodialysis
- PMID: 36977892
- PMCID: PMC10047466
- DOI: 10.1007/s10157-023-02342-0
Blunted humoral immune response to the fourth dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in patients undergoing hemodialysis
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the impact of a fourth dose of BNT162b2 vaccine (Comirnaty®, Pfizer-BioNTech) on anti-SARS-CoV-2 (anti-S IgG) antibody titers in patients receiving hemodialysis (HD) and healthcare workers (HCWs).
Methods: A multi-institutional retrospective study at five dialysis clinics in Japan was conducted using 238 HD patients and 58 HCW controls who received four doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Anti-S IgG titers were measured at 1, 3, and 6 months after the second dose, at 1 and 5/6 months after the third dose, and at 1 month after the fourth dose of vaccine.
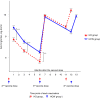
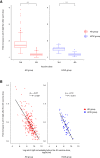
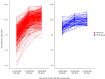
Results: The log anti-S IgG titers of the HD patients after the second vaccination were significantly lower than those of the control group, but equalized 1 month after the third vaccination: 9.94 (95% CI 9.82-10.10) vs. 9.81 (95% CI 9.66-9.96), (P = 0.32). In both groups, the fold-increase in anti-S IgG titers was significantly lower after the fourth dose than after the third dose of vaccine. In addition, there was a strong negative correlation between antibody titers 1 month after the fourth vaccination and antibody titers immediately before the vaccination. In both groups, the waning rate of anti-S IgG titers from the post-vaccination peak level after the third vaccine dose was significantly slower than that after the second dose.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that the humoral immune response was blunted after the fourth dose of the conventional BNT162b2 vaccine. However, multiple vaccinations could extend the window of humoral immune protection.
Keywords: Antibody; BNT162b2; Hemodialysis; SARS-CoV-2; Spike protein; Vaccine.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to The Japanese Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

