The use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers may relate to the survival and walking ability in geriatric patients with hip fractures: a 1-year follow-up study
- PMID: 36978079
- PMCID: PMC10045946
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-023-06362-5
The use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers may relate to the survival and walking ability in geriatric patients with hip fractures: a 1-year follow-up study
Abstract
Background: Many elder patients with hip fractures also suffered from hypertension. This study aims to explore the relationship between the use of ACEI or ARB and the outcomes of geriatric hip fractures.
Methods: All the patients were divided into four groups: non-users without hypertension, non-users with hypertension, ACEI users, and ARB users. The outcomes of patients in different groups were compared. LASSO regression and univariable Cox analysis were used for variable screening. Then Cox models and Logistics models were established to identify the relationships between the use of RAAS inhibitors and outcomes.
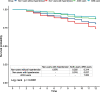
Results: ACER users (p = 0.016) and ARB users (p = 0.027) had a significantly lower survival probability than the non-users with hypertension. Non-users without hypertension, ACEI users, and ARB users may face lower 6-month and 1-year mortalities and higher 6-month and 1-year free walking rates compared with non-users with hypertension.
Conclusion: Patients with the use of ACEI or ARB may face a better prognosis of hip fractures.
Keywords: ACEI; ARB; Hip fractures; Hypertension; Prognosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- McHugh MA, Wilson JL, Schaffer NE, Olsen EC, Perdue A, Ahn J, et al. Preoperative Comorbidities Associated With Early Mortality in Hip Fracture Patients: A Multicenter Study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023;31(2):81–86. - PubMed
-
- Liu M, Ji S, Yang C, Zhang T, Han N, Pan Y, et al. Prealbumin as a nutrition status indicator may be associated with outcomes of geriatric hip fractures: a propensity score matching and 1-year follow-up study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022;34(12):3005–3015. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

