Plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PDEVs) in nanomedicine for human disease and therapeutic modalities
- PMID: 36978093
- PMCID: PMC10049910
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-023-01858-7
Plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PDEVs) in nanomedicine for human disease and therapeutic modalities
Abstract
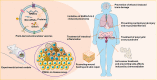
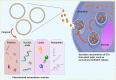
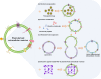
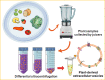
Background: The past few years have witnessed a significant increase in research related to plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PDEVs) in biological and medical applications. Using biochemical technologies, multiple independent groups have demonstrated the important roles of PDEVs as potential mediators involved in cell-cell communication and the exchange of bio-information between species. Recently, several contents have been well identified in PDEVs, including nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and other active substances. These cargoes carried by PDEVs could be transferred into recipient cells and remarkably influence their biological behaviors associated with human diseases, such as cancers and inflammatory diseases. This review summarizes the latest updates regarding PDEVs and focuses on its important role in nanomedicine applications, as well as the potential of PDEVs as drug delivery strategies to develop diagnostic and therapeutic agents for the clinical management of diseases, especially like cancers.
Conclusion: Considering its unique advantages, especially high stability, intrinsic bioactivity and easy absorption, further elaboration on molecular mechanisms and biological factors driving the function of PDEVs will provide new horizons for the treatment of human disease.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell-cell communication; Human diseases; Nanomedicine; Plant-derived extracellular vesicles.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic potential and pharmacological significance of extracellular vesicles derived from traditional medicinal plants.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 1;14:1272241. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1272241. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38108066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Exciting Potential as the Future of Next-Generation Drug Delivery.Biomolecules. 2023 May 15;13(5):839. doi: 10.3390/biom13050839. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in plant-derived extracellular vesicles: isolation, composition, and biological functions.Food Funct. 2024 Nov 25;15(23):11319-11341. doi: 10.1039/d4fo04321a. Food Funct. 2024. PMID: 39523827 Review.
-
Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Frontier in Cancer Therapeutics.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;14(16):1331. doi: 10.3390/nano14161331. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic application and potential mechanism of plant-derived extracellular vesicles in inflammatory bowel disease.J Adv Res. 2025 Feb;68:63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.01.035. Epub 2024 Feb 9. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38341033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-derived extracellular nanovesicles: a promising biomedical approach for effective targeting of triple negative breast cancer cells.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 17;12:1390708. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1390708. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38952670 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-derived exosome-like nanovesicles: A novel nanotool for disease therapy.Heliyon. 2024 May 3;10(9):e30630. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30630. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38765146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging plant-derived nanovesicles for advanced nucleic acid-based gene therapy.Theranostics. 2025 Jan 1;15(1):324-339. doi: 10.7150/thno.104507. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 39744221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the dynamic trends of plant-derived exosome nanovesicles-based theranostics: through bibliometric and visualized analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 24;12:1553915. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1553915. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40630491 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-based delivery strategies for tumor therapy: an update on modification, loading, and clinical application.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jan 28;22(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02298-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38281957 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

